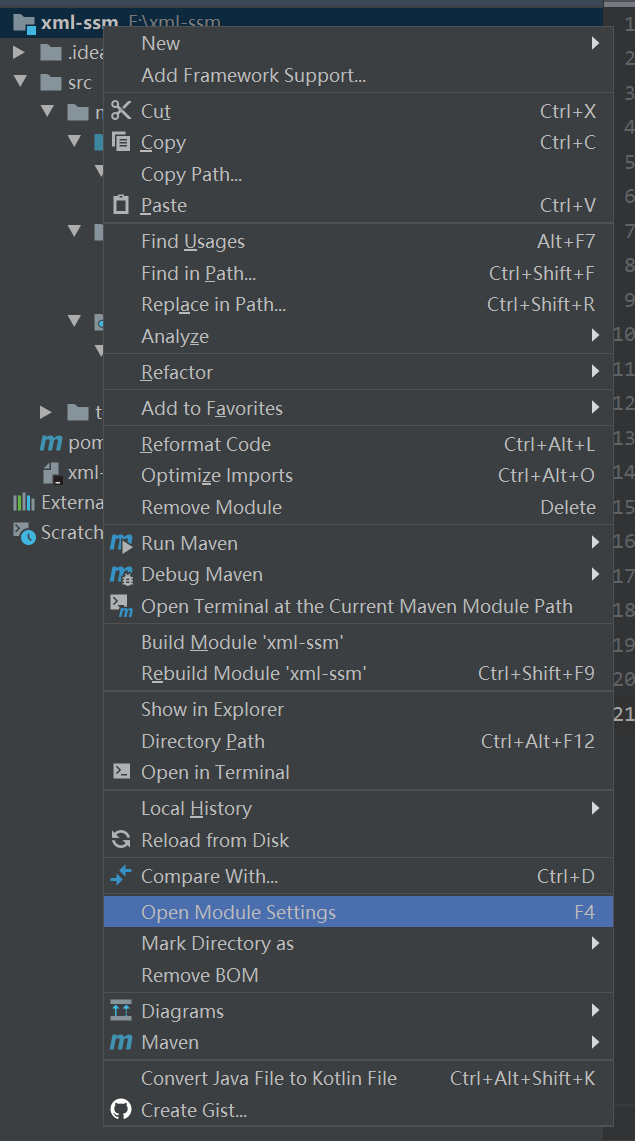
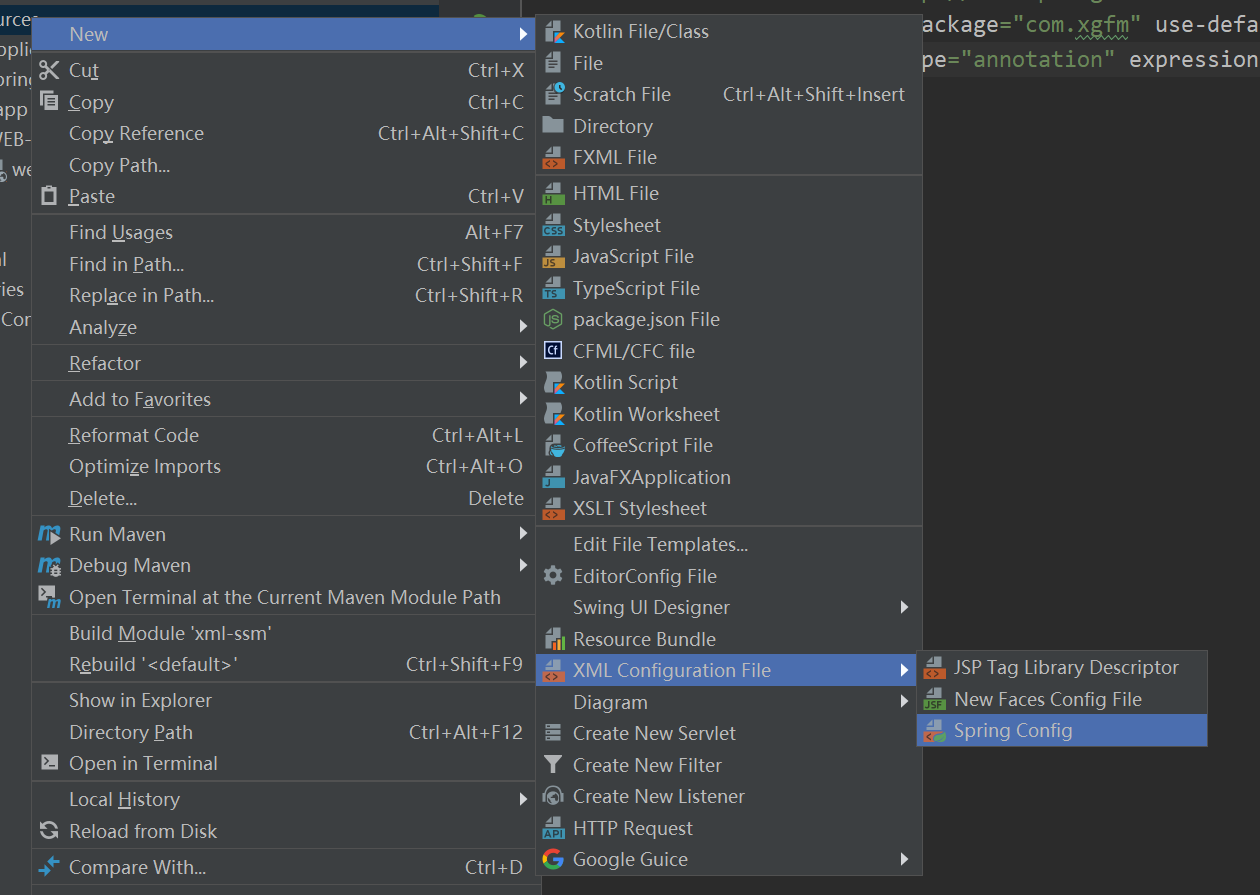
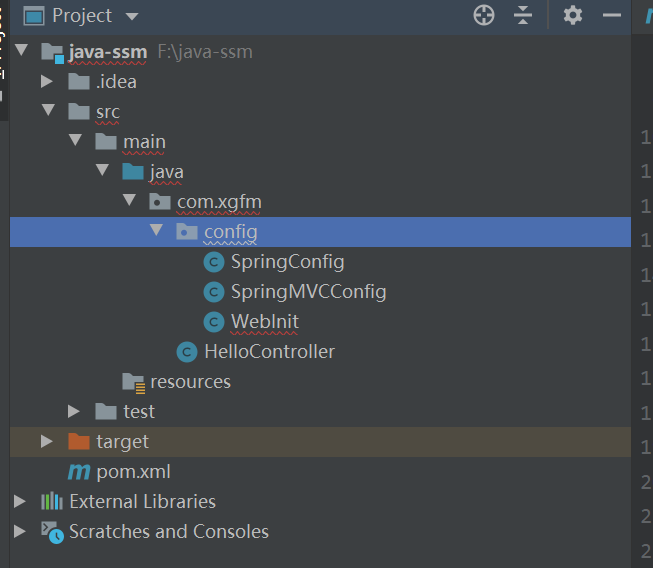
xml-ssm文件配置
在maven中配置springmvc
1 2 3 4 5 <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework</groupId > <artifactId > spring-webmvc</artifactId > <version > 5.3.1</version > </dependency >
在项目处右键,选择Open Module Setting,创建resourcs和webapp等标准的文件。
创建controller
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;@RestController public class HelloController {@GetMapping("/hello") public String hello () {return "hello world" ;
在resources处创建Spring config文件
创建applicationContext.xml和spring-serlvet.xml文件
applicationContext.xml文件配置
1 2 3 <context:component-scan base-package ="com.xgfm" use-default-filters ="true" > <context:exclude-filter type ="annotation" expression ="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller" /> </context:component-scan >
spring-servlet.xml文件配置
1 2 3 4 <context:component-scan base-package ="com.xgfm" use-default-filters ="false" > <context:include-filter type ="annotation" expression ="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller" /> </context:component-scan > <mvc:annotation-driven />
web.xml配置
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 <context-param > <param-name > contextConfigLocation</param-name > <param-value > classpath:applicationContext.xml</param-value > </context-param > <listener > <listener-class > org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class > </listener > <servlet > <servlet-name > springmvc</servlet-name > <servlet-class > org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class > <init-param > <param-name > contextConfigLocation</param-name > <param-value > classpath:spring-servlet.xml</param-value > </init-param > </servlet > <servlet-mapping > <servlet-name > springmvc</servlet-name > <url-pattern > /</url-pattern > </servlet-mapping >
HelloService
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;@Service public class HelloService {@GetMapping("/hello") public String hello () {return "hello ssm" ;
HelloController
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;@RestController public class HelloController {@Autowired @GetMapping("/hello") public String hello () {"hello=" +hello);return "hello world" ;
然后运行tomcat就可运行了
java-ssm文件配置
在maven中配置springmvc
1 2 3 4 5 <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework</groupId > <artifactId > spring-webmvc</artifactId > <version > 5.3.1</version > </dependency >
编写HelloController
编写java写的config组件
config文件如图
踩坑记录1
在pom.xml中没写以下代码,导致无法配置tomcat
1 <packaging > war</packaging >
踩坑记录2
webInit
报错:目前未解决
1 ServletRegistration.Dynamic springMVC = servletContext.addServlet("springMVC" , new DispatcherServlet (ctx));
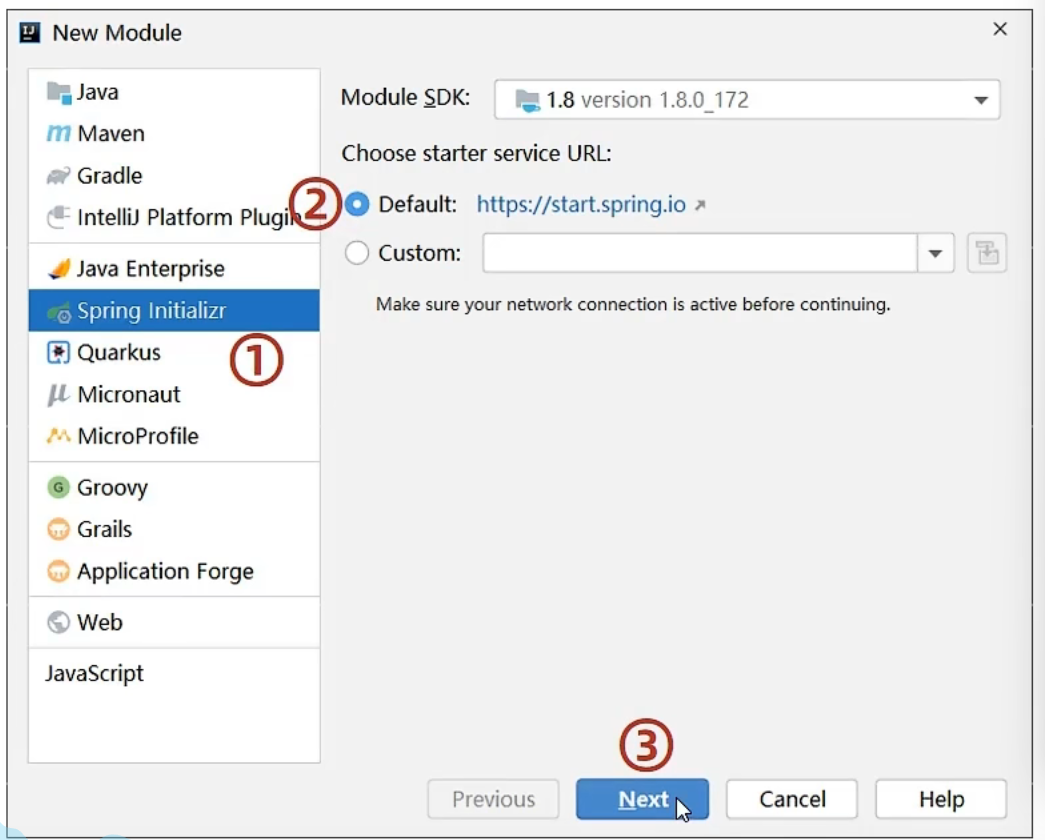
springboot创建
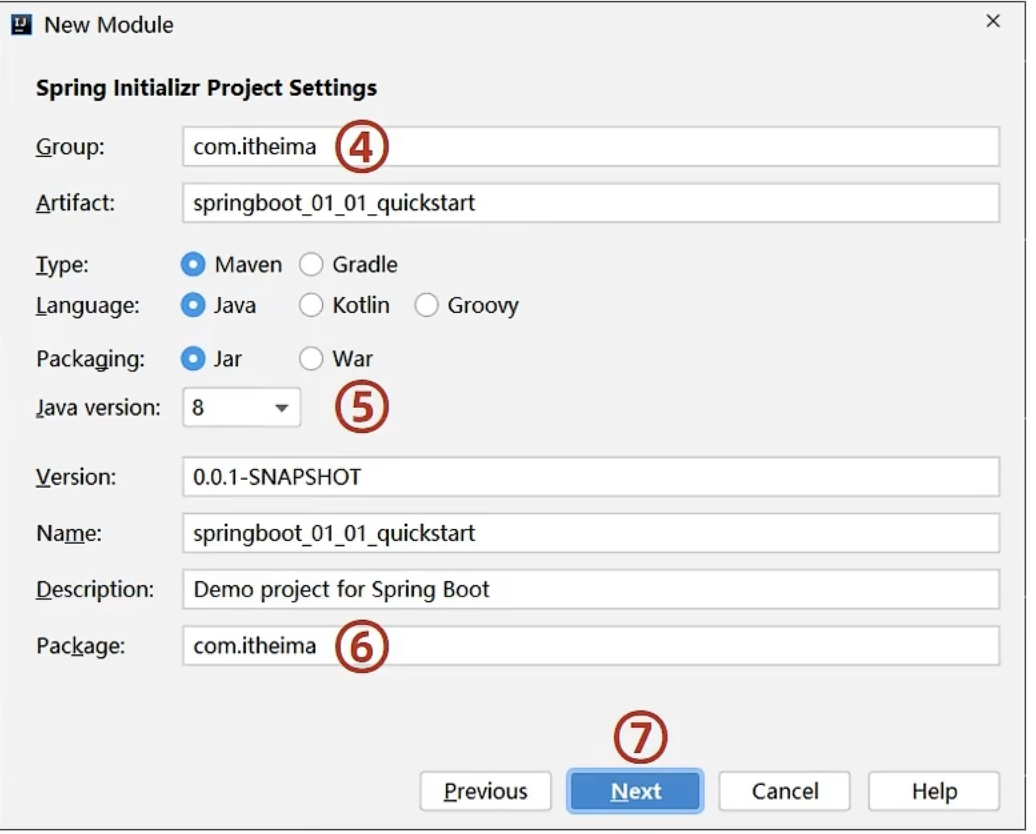
创建新模块,选择Spring Initializr,并且配置模块相关的基本信息
4是取包名
5选择与之相对应的jdk版本
6.7日常下一步
然后选择Spring web,并且版本号选择2.x.x开头的,高版本的JDK8不适配
另附其他俩种方法:
在线创建:https://start.spring.io
Maven改造
也可以使用国内阿里云提供的start站
http://start.aliyun.com
Springboot部分注解 @SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan
@EnableAutoConfiguration @Import注解
在原生的spring Framework中,组件装配逐步升级
spring2.5+ @Component
spring3.0+ @Configuration+@Bean
spring3.1+ @EnableXXX+@Import
@ComponentScan注解
对启动项进行包扫描
Maven标签–parent
定义java的编译版本
定义项目编码格式
定义依赖的版本号
项目打包配置
自动化的资源过滤
自动化的插件配置
Web容器配置 springboot支持三个服务
目前使用servlet技术栈
可以使用的服务器分别是tomcat,jetty和undertow
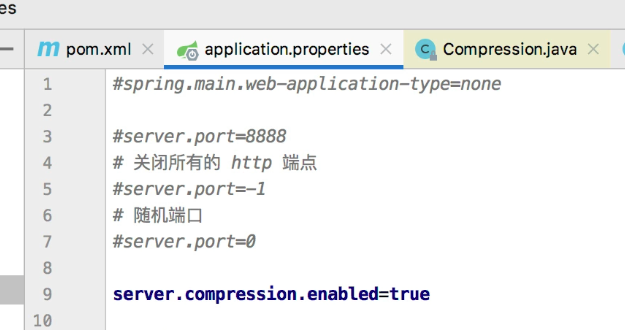
选择web容器配置 在application.prooerties中配置
第一行为web容器选择
server.port代表端口的选择
最后一行为是否压缩容器
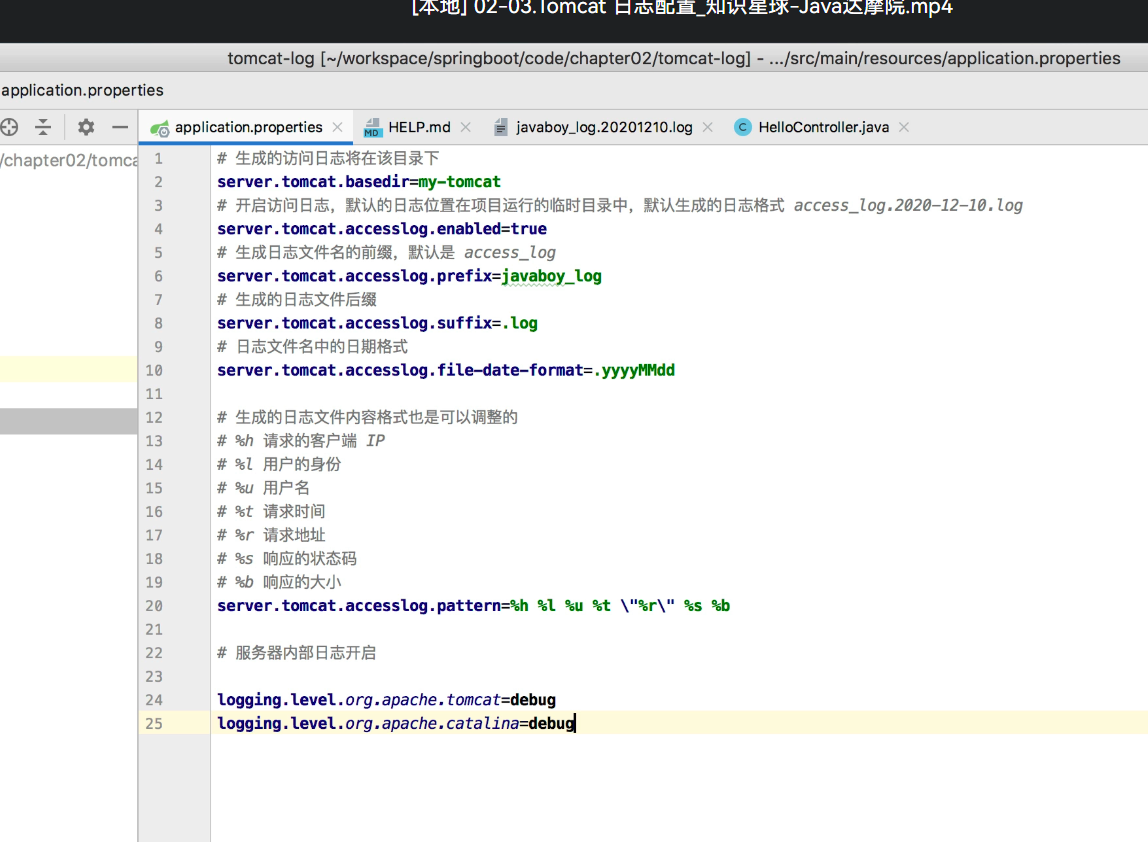
tomcat容器配置 开启访问日志,默认的日志位置在项目运行的临时目录中
日志设置语句如下
HTTPS证书配置
生成https证书
1 keytool -genkey -alias myhttps -keyalg RSA -keysize 2048 -keystore xgfm_key.p12 -validity 365
2.在application.properties中配置证书
1 2 3 server.ssl.key-alias =myhttps server.ssl.key-store =classpath:xgfm_key.p12 server.ssl.key-store-password =111111
3.创建config文件
配置tomcat文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 package com.xgfm.demo02.config;import org.apache.catalina.Context;import org.apache.catalina.connector.Connector;import org.apache.tomcat.util.descriptor.web.SecurityCollection;import org.apache.tomcat.util.descriptor.web.SecurityConstraint;import org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.TomcatServletWebServerFactory;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;@Configuration public class TomcatConfig {@Bean tomcatServletWebServerFactory () {TomcatServletWebServerFactory factory = new TomcatServletWebServerFactory (){@Override protected void postProcessContext (Context context) {new SecurityConstraint ();"CONFIDENTIAL" );SecurityCollection collection = new SecurityCollection ();"/*" );return factory;private Connector myConnectors () {Connector connector = new Connector ("org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11NioProtocol" );"http" );8081 );false );8080 );return connector;
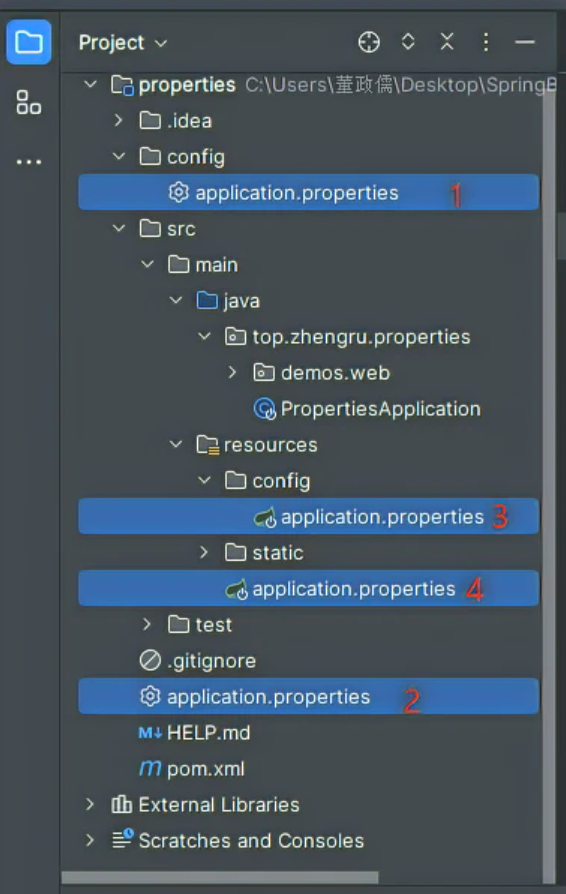
配置文件名称和路径 配置文件有4个位置
-config/application.properties
-application.properties
-src/main/resources/config/application.properties
-src/main/resources/application.properties
(偷一张我帅气班长的图)
四个的优先级是依次降低的
同时可以进行自定义配置文件路径
注意配置文件的路径要以/结尾
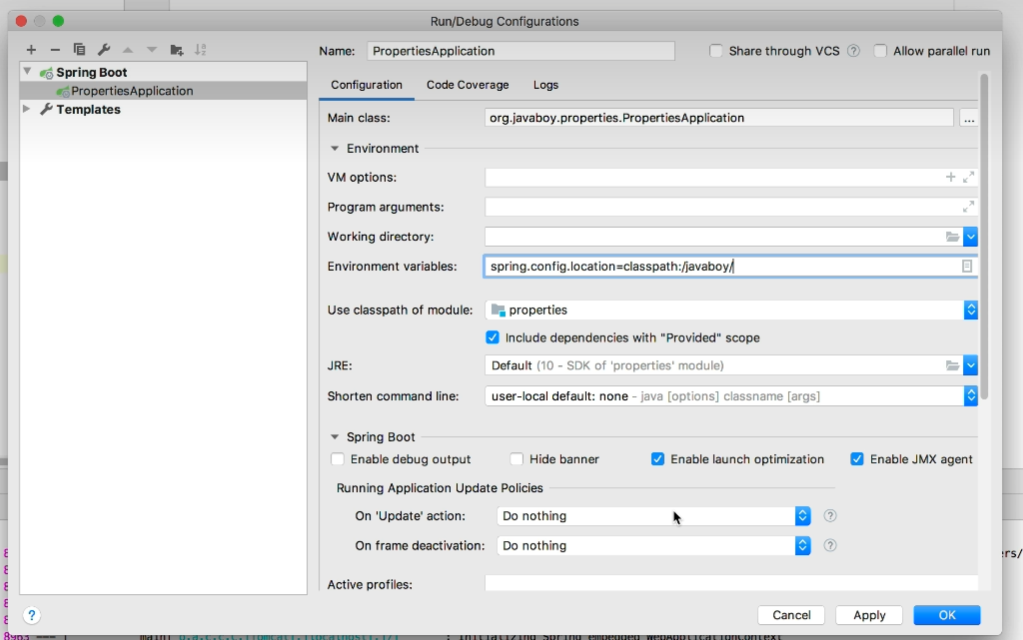
如果自定义配置文件的路径,打包完运行jar包的时候,要用spring.config.loaction进行指定
例如:
1 java -jar xxx.jar --spring.config.location=calsspath:/xgfm/
但这些一般情况下是没有必要的
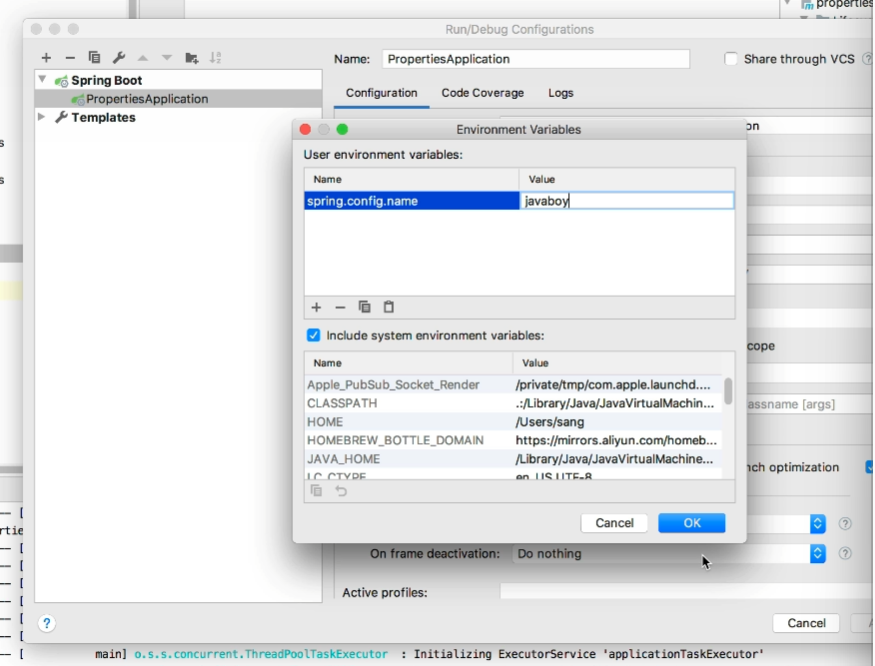
文件名称也是可以进行更换的
比如创建xgfm.properites
然后在project setting同样进行配置
文件中有一个properites就可以了
如果自定义文件的名称也要在运行jar包的时候,用spring.config.name进行指定
1 java -jar xxx.jar --spring.config.name=xgfm
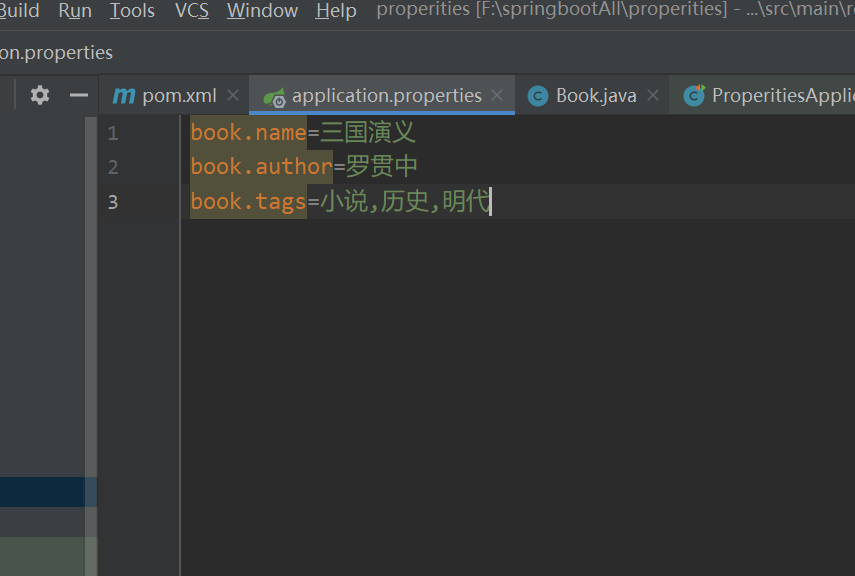
普通属性注入 为了避免中文乱码,要在设置中的editor-file Encodings中的文件编码为UTF-8
可以在application.properties中输入属性,在model处使用,数组属性需要使用英文逗号进行分隔
使用value注解,其中数组也是可以注入的
这是spring的普通属性注入,与springboot无太大关系
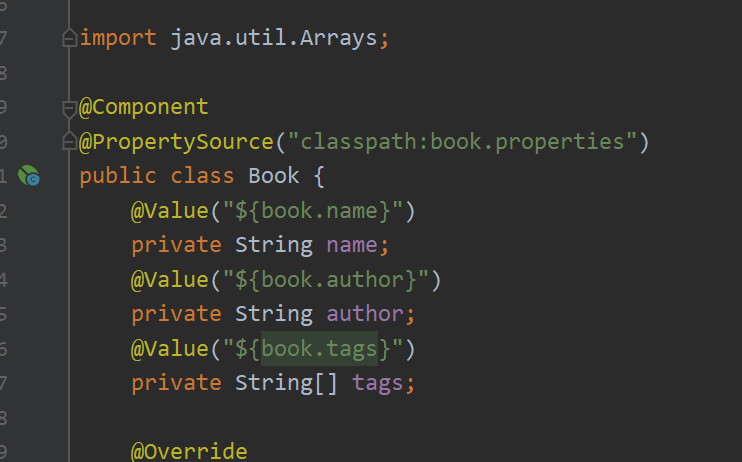
并且在有的时候会将这些注入写在其他的properties中,避免application.properties过于臃肿,然后会写在一个xxx.properties之中,这时候就需要手动加载该properties
1 @PropertySource("classpath:xxx.properties")
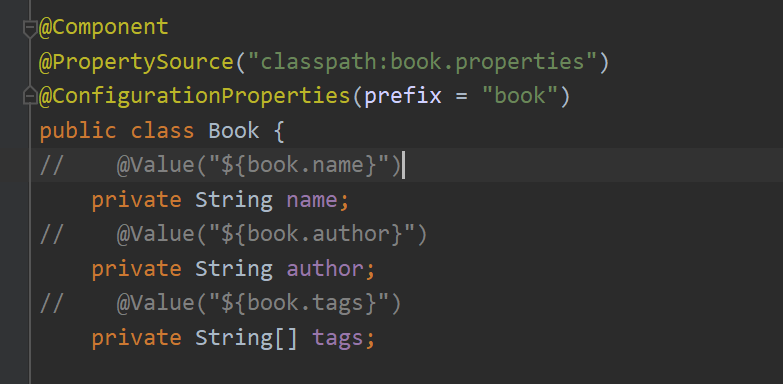
类型安全的属性注入 使用以下语句进行类型安全的属性注入
1 @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "xxx")
xxx为文件的名称前缀,然后就会自动注入
使用类型安全的属性注入的代码案例如下
properties引用Maven中的配置 在properties中引用Maven中的配置,应该使用@...@,而不是${….},不然会和本地起冲突
使用短命令行参数 在终端启动
1 java -jar properties-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar --server.port=8081
如果省略server将不会生效,如果想要能够生效,需要在application.properties中配置以下信息
这个情况下,以下代码能够有效
1 java -jar properties-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar --port=8081
但是如果配置了properties,但没有输入,则会报错,那么我们就需要这么写properties
1 server.port =${port:8080}
这种情况下,如果没有port输入,则自动使用8080作为端口启动
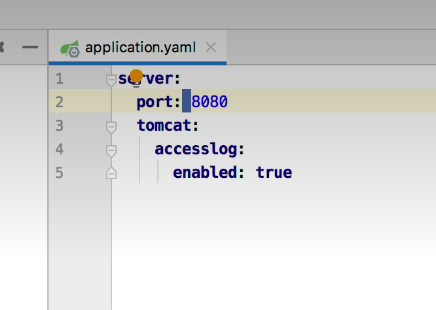
YAML配置 将application的文件后缀更改为yaml或者yml
yaml配置是有顺序的,而properties是无序的,这是两者的差距,并且yaml支持自动配置除application以外的文件名称,改文件名是完全没有必要的
yaml配置是比较自动化的,编写属性会有跳出的提示
并且强制要求:后要有空格,否则将会报错,这个空格一定不能少
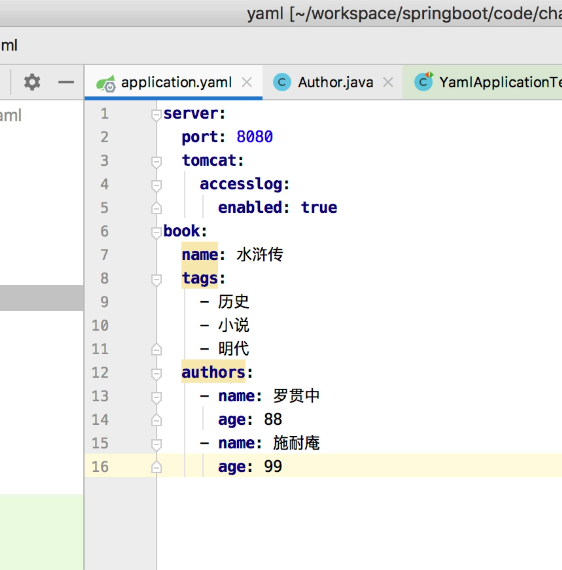
案例:
同样的book的属性注入
要这也进行编写,注意小说后都有一个空格
案例中分别有单个属性,普通数组,对象数组的注入
注意格式的要求
内省机制 属性注入是根据get和set方法进行判断该使用哪个get方法进行注入。这是利用了java中的反射机制(这里也只是提一嘴),并且该机制与yaml和properties无关,是自带的
Profile 不同情况下要使用的环境是不同的,重复更改环境会很麻烦,springboot准备了生产环境切换
然后再application.properties中配置生产环境
1 2 3 spring.profiles.active =dev spring.profiles.active =prod spring.profiles.active =test
JAVA日志配置 日志框架分为日志门面和日志实现
日志配置文章
这里需要了解清楚日志体系
SpringBoot日志配置 springboot的默认日志门面是Logback
还是这个哦
日志配置文章
SpingBoot+Thymeleaf Spring Boot+Thymeleaf
传统Java模板引擎不同的是,Thymeleaf支持HTML原型
Thymeleaf实践 创建项目时候需要导入模板
选择以下俩项
然后在application.properties中导入以下设置
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 spring.thymeleaf.cache =true spring.thymeleaf.check-template =true spring.thymeleaf.check-template-location =true spring.thymeleaf.content-type =text/html spring.thymeleaf.enabled =true spring.thymeleaf.encoding =UTF-8 spring.thymeleaf.excluded-view-names =spring.thymeleaf.mode =HTML5 spring.thymeleaf.prefix =classpath:/templates/ spring.thymeleaf.suffix =.html
编写User类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 package com.xgfm.thymeleaf;public class User {private Integer id;private String username;private String address;public Integer getId () {return id;public void setId (Integer id) {this .id = id;public String getUsername () {return username;public void setUsername (String username) {this .username = username;public String getAddress () {return address;public void setAddress (String address) {this .address = address;
编写UserController
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 package com.xgfm.thymeleaf;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.ui.Model;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List;@Controller public class UserController {@GetMapping("/hello") public String index (Model model) {new ArrayList <>();for (int i=0 ;i<10 ;i++){new User ();"xgfm" +i);"www.xgfm.com" +i);"users" ,users);return "hello" ;
创建hello.html(此处的html有遍历,可以借鉴一下)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" xmlns:th ="http://www.thymeleaf.org" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > Title</title > </head > <body > <table border ="1" > <tr th:each ="u : ${users}" > <td th:text ="${u.id}" > </td > <td th:text ="${u.username}" > </td > <td th:text ="${u.address}" > </td > </tr > </table > </body > </html >
Thymeleaf手动渲染 自动渲染时直接返回到前端页面的
为了方便编写测试类进行
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 @SpringBootTest class ThymeleafApplicationTests {@Autowired @Test void contextLoads () {Context ctx = new Context ();"username" ,"佛耶戈" );"position" ,"太痛了" );"salary" ,"600000" );String mail = templateEngine.process("mail" , ctx);
控制台输出结果
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > Title</title > </head > <body > <p > Hello,欢迎!<span > 佛耶戈</span > 加入破败军团,您的入职信息如下</p > <table > <tr > <td > 职位</td > <td > 太痛了</td > </tr > <tr > <td > 薪水</td > <td > 600000</td > </tr > </table > </body > </html >
这样就可以手动渲染结果了
目前还有一些莫名其妙的报错,尚未解决,另外还不知道怎么把手动渲染结果直接输出到前端页面
先放一下
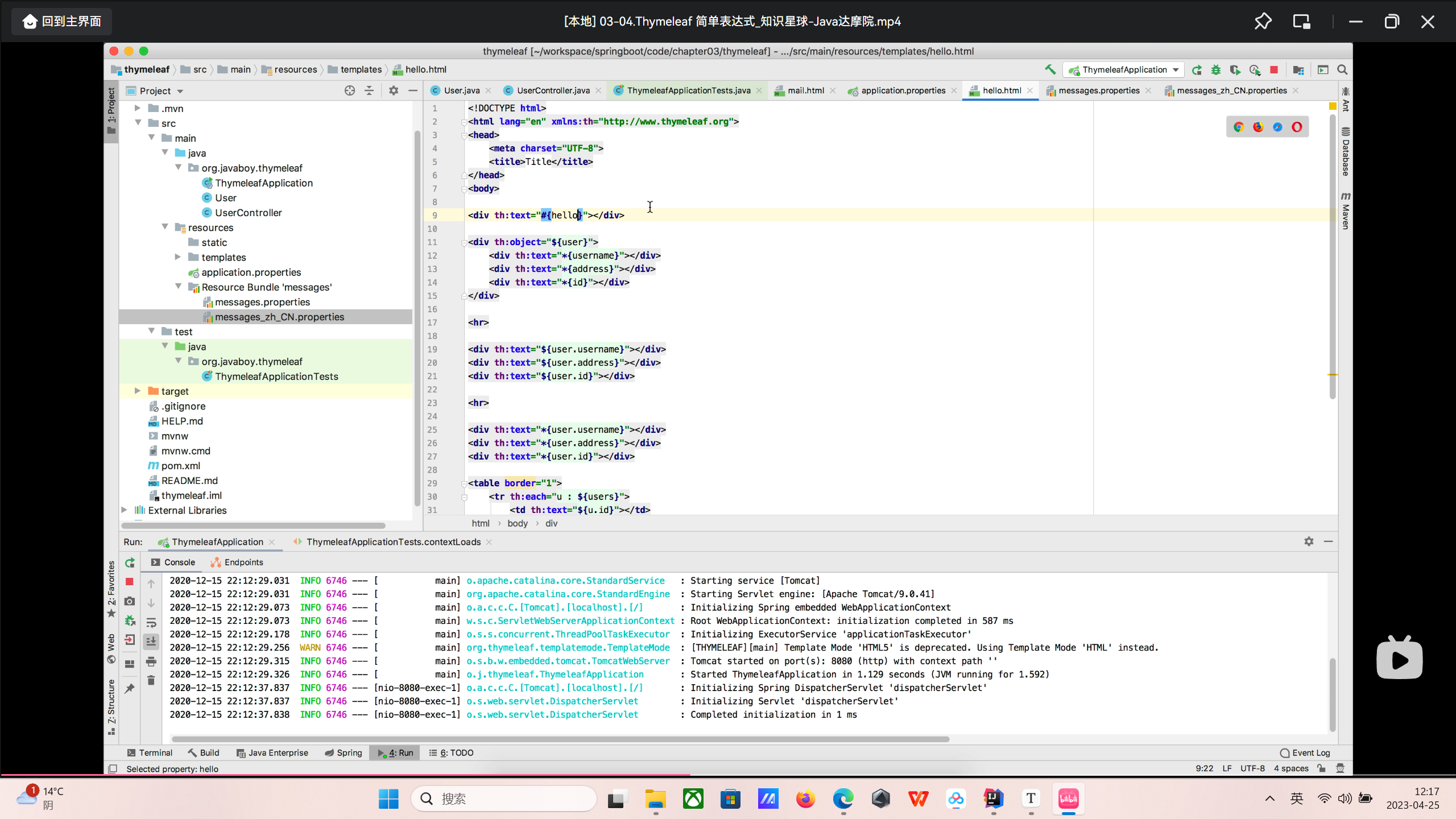
Thymeleaf简单表达式 表达式语法包含如下
${} 最普通和常见的引用类型
可以直接进行引用
1 2 3 4 5 <div th:object ="${user}" > <div th:text ="*{username}" > </div > <div th:text ="*{address}" > </div > <div th:text ="*{id}" > </div > </div >
*{}和${}用起来的效果是相近的
*{} 与上面的${}效果类似,所以用起来是没有很大差距的
#{} 主要用于国际化
messages.properties
message_zh_CN.properties
1 <div th:text ="#{hello}" > </div >
根据浏览器的语言环境进行选择
中文环境选择message_zh_CN.properties,英文环境选择messages.properties
@{} 引用URL地址
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 //绝对地址<script th:src ="@{https://localhost:8080/hello.js}" > </script > <script th:src ="@{~/hello.js}" > </script > <script th:src ="@{//localhost:8080/hello.js}" > </script > <script th:src ="@{//localhost:8080/hello.js(name='zhengru',age=99)}" > </script > <script th:src ="@{/hello.js}" > </script >
Thymeleaf各种表达式 字面量
文本字面量
数字字面量
布尔字面量
Null字面量
字面量标记
文本运算 如果字符串中包含EL表达式输出的变量,也可以使用另一种简答的方式,叫做字面量置换
即使用||替换”…”+”…”
例子
1 2 <div th:text ="'hello'+${user.username}" > </div > <div th:text =|hello${user.username}| "> </div >
这俩都能一起使用
布尔运算
二元运算符:and, or
布尔非(一元运算符):!, not
比较和相等 表达式里的值可以使用 >, <, >= 和 <= 符号比较。== 和 != 运算符用于检查相等(或者不相等)。注意 XML规定 < 和 > 标签不能用于属性值,所以应当把它们转义为 < 和 >
如果不想转义,也可以使用别名:gt (>);lt (<);ge (>=);le (<=);not (!)。还有 eq (==), neq/ne (!=)
条件运算符 类似于我们 Java 中的三目运算符
内置对象 基本内置对象:
#ctx:上下文对象。
#vars: 上下文变量。
#locale:上下文区域设置。
#request:(仅在 Web 上下文中)HttpServletRequest 对象。
#response:(仅在 Web 上下文中)HttpServletResponse 对象。
#session:(仅在 Web 上下文中)HttpSession 对象。
#servletContext:(仅在 Web 上下文中)ServletContext 对象。
实用内置对象:
#execInfo:有关正在处理的模板的信息。
#messages:在变量表达式中获取外部化消息的方法,与使用#{…}语法获得的方式相同。
#uris:转义URL / URI部分的方法
#conversions:执行配置的转换服务(如果有)的方法。
#dates:java.util.Date对象的方法:格式化,组件提取等
#calendars:类似于#dates但是java.util.Calendar对象。
#numbers:用于格式化数字对象的方法。
#strings:String对象的方法:contains,startsWith,prepending / appending等
#objects:一般对象的方法。
#bools:布尔评估的方法。
#arrays:数组方法。
#lists:列表的方法。
#sets:集合的方法。
#maps:地图方法。
#aggregates:在数组或集合上创建聚合的方法。
#ids:处理可能重复的id属性的方法(例如,作为迭代的结果)。
相对应的方法可以在属性值中查看
设置属性值 1 <img th:attr ="src=@{/1.png},title=${user.username},alt=${user.username}" >
1 <img src ="/myapp/1.png" title ="javaboy" alt ="javaboy" >
1 <img th:src ="@{/1.png}" th:alt ="${user.username}" th:title ="${user.username}" >
1 <img th:src ="@{/1.png}" th:alt-title ="${user.username}" >
遍历 遍历的状态支持
index 当前索引从0开始
count 当前索引从1开始
size 被遍历的元素数量
current 每次遍历的遍历变量
odd 当前的遍历是偶数还是奇数
first 当前是否为第一次遍历
last 当前是否为最后遍历
Thymeleaf分支语句 th:if语句,该判断语句不仅只接受布尔值,其他类型的值同样也接受
true|false输出如下
th:unless语句
就是th:if语句的取反
th:switch,case语句
情况判断语句,例如
1 2 3 4 5 //在外面包裹一层遍历语句<td th:switch ="${state.add}" > <span th:case ="true" > odd</span > <span th:case ="*" > even</span > </td >
本地变量 可以使用th:with定义一个本地变量,前面已经提到并且使用过了,这里就不再过多赘述了
内联 可以使用属性将数据放入页面模板之中,但是很多时候内联的方式看起来更加直观和简洁一些,并且拼接也会显得更加自然一些,例子
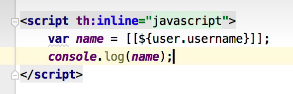
1 <div > hello [[${user.username}]]</div >
[[...]] 对应于 th:text (结果会是转义的 HTML)
[(...)]对应于 th:text,它不会执行任何的 HTML 转义
1 2 3 4 <div th:with ="str='hello <strong>javaboy</strong>'" > <div > [[${str}]]</div > <div > [(${str})]</div > </div >
显示结果分别是
1 2 // 第一行为hello <strong>javaboy</strong>// 第二行为hello javaboy(javaboy为加粗后的)
Spring Boot+Thymeleaf
总的来说,可以多看几遍该文章
在script中使用,要这样使用
SpingBoot+Freemarker 经典之开篇给文章!
SpingBoot+Freemarker
Freemarker不是面向最终用户的,而是一个java类库,可以将其作为以一个普通的组件嵌入到我们产品之中的
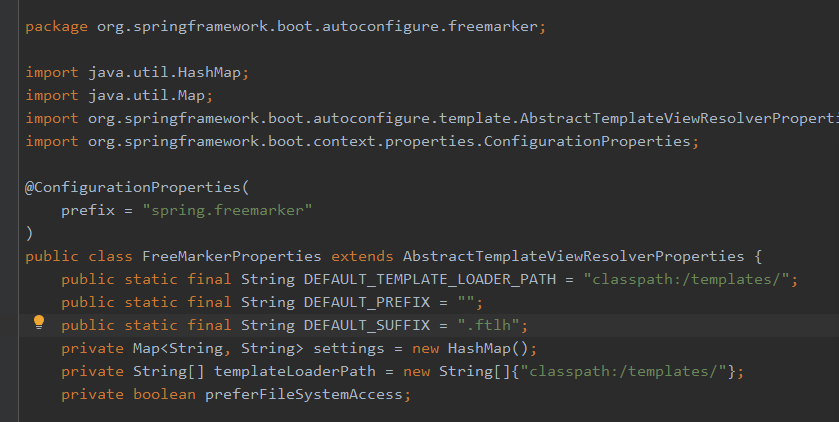
模板的后缀为.ftlh
FreeMarkerProperties中则配置了Freemarker的基本信息,例如模板位置在 classpath:/templates/ ,再例如模板后缀为 .ftlh,那么这些配置我们以后都可以在application.properties中进行修改
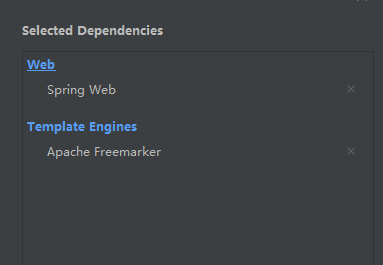
freemarker实践 创建项目时候需要导入模板
选择以下俩项
和thymeleaf有点类似的说实话
如果需要修改模板文件位置,可以在application.properties中进行配置
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 spring.freemarker.allow-request-override =false spring.freemarker.allow-session-override =false spring.freemarker.cache =false spring.freemarker.charset =UTF-8 spring.freemarker.check-template-location =true spring.freemarker.content-type =text/html spring.freemarker.expose-request-attributes =false spring.freemarker.expose-session-attributes =false spring.freemarker.suffix =.ftl spring.freemarker.template-loader-path =classpath:/templates/
配置文件按照顺序依次解释如下:
HttpServletRequest的属性是否可以覆盖controller中model的同名项
HttpSession的属性是否可以覆盖controller中model的同名项
是否开启缓存
模板文件编码
是否检查模板位置
Content-Type的值
是否将HttpServletRequest中的属性添加到Model中
是否将HttpSession中的属性添加到Model中
模板文件后缀
模板文件位置
Freemarker直接输出值 可以直接输出的字符串(即不需要转义的)
1 <div > ${"hello,我是直接输出的语句"}</div >
需要转义的输出字符串看眼添加r的标记
定义变量语句
可以看看freemarker的内联语句,同样是十分高效的
认识主流JSON框架 springMVC框架中,Jackson和gson已经自动配置好了。
HttpMessageConverter
转换器:对象——>json,json——>对象
所有的json工具都会提供各自的HttpMessageConverter
Spring boot 整合Jackson @JsonProperty 指定属性序列化/反序列化时的名称,默认名称就是属性名
1 2 @JsonProperty(value="aaaage",index=99) private Integer age;
value为属性名称, index是json序列化和反序列化的顺序索引
@JsonIgnore 忽略掉相对应的数据
并且序列化和反序列化的时候都会忽略掉该字段
1 2 @JsonIgnore private String address;
@JsonIgnoreProperties() 括号中输入value数组,批量忽略数组
1 @JsonIgnoreProperties({"birthday","address"})
这个是格式化输入数据
1 2 @JsonFormat(pattern ="yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss",timezone = "Asia/Shanghai") private Date birthday;
日期格式化,timezone是日期格式化
使用MVCConfig进行内置配置 创建一个WebMvcCofig文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 @Configuration public class WebMvcConfig {@Bean objectMapper () {ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper ();new SimpleDateFormat ("yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss" ));return om;
在config中设置,这样可以避免重复书写,该工程中所有的实体类的时间的格式都会统一成写的pattern。
Spring boot 整合gson 首先需要将jackson的包从maven中排除出去
使用如下代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 <exclusions > <exclusion > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-json</artifactId > </exclusion > </exclusions >
添加在dependency中排除相对应的artifactId的jar包
然后添加gson的依赖
1 2 3 4 <dependency > <groupId > com.google.code.gson</groupId > <artifactId > gson</artifactId > </dependency >
gson的格式可以在application中进行配置
properties配置 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 spring.gson.date-format =yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss spring.gson.disable-html-escaping =true spring.gson.disable-inner-class-serialization =false spring.gson.enable-complex-map-key-serialization =spring.gson.exclude-fields-without-expose-annotation =spring.gson.field-naming-policy =spring.gson.generate-non-executable-json =spring.gson.serialize-nulls =
或者也可以使用
WebMvcConfig配置 会重载原本的处理方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 @Configuration public class WebMvcConfig {@Bean gsonBuilder () {new GsonBuilder ();"yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss" );return gsonBuilder;
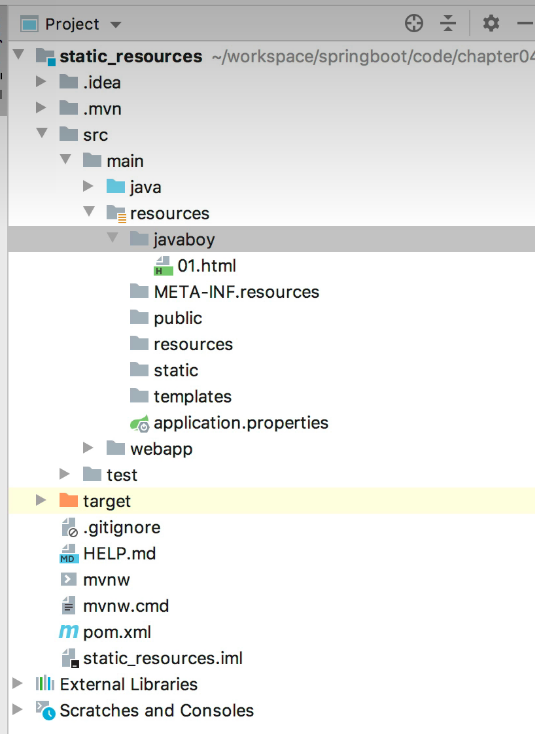
Spring boot 处理静态资源
springboot的静态资源默认存放在static下
并且访问静态资源时不需要添加static
静态资源放置的位置:
/META-INF/resources/
/resources/
/static/
/public/
在webapp下直接放置(十分不常用)
优先级从上向下降低
自定义静态资源配置 如果没有配置,直接访问resources中的资源会被拦截,并且报错404
properties 文件配置 这时候就需要手动配置以下文件
1 2 spring.web.resources.static-locations =classpath:/ spring.mvc.static-path-pattern =/**
第一行配置表示定义资源位置,第二行配置表示定义请求 URL 规则
这样能够通过访问localhost:8080/javaboy/01.html
如果在properties下配置的是classpath:/javaboy/
那么需要访问localhost:8080/01.html
Java代码配置 创建一个WebMvcConfig.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 @Configuration public class WebMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {@Override public void addResourceHandlers (ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {"/xg/**" ).addResourceLocations("classpath:/xgfm/" );
用java代码进行配置的意思就是用addResourceHandler的内容来映射addResourceLocations的内容。
在上面里的例子中,即可通过访问 localhost:8080/xg/01.html来访问resources下的xgfm包中的01.html静态资源
Spring boot单文件上传 //该内容用static_resources的工程文件一起练习
首先写一个提交文件的页面
1 2 3 4 <form action ="/upload" method ="post" enctype ="multipart/form-data" > <input type ="file" name ="file" > <input type ="submit" > </form >
写一个controller处理
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 @RestController public class FileUploadController {new SimpleDateFormat ("/yyyy/mm/dd/" );@PostMapping("/upload") public String upload (MultipartFile file, HttpServletRequest request) {String realPath = request.getServletContext().getRealPath("/" );String format = sdf.format(new Date ());new File (path);if (!folder.exists()){String oldName = file.getOriginalFilename();String newName = UUID.randomUUID().toString()+oldName.substring(oldName.lastIndexOf("." ));try {new File (folder,newName));"://" +request.getServerName()+":" +request.getServerPort()+format+newName;return s;catch (IOException e) {return "" ;
同时,还可以在properties中配置其他信息
比如限制单个文件的大小和限制所有文件的大小
1 2 spring.servlet.multipart.max-file-size =1MB spring.servlet.multipart.max-request-size =10MB
Spring boot多文件上传 合并多文件 在controller的形参中用数组接受输入的文件,再用for循环遍历
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 @RestController public class FileUploadController2 {new SimpleDateFormat ("/yyyy/mm/dd/" );@PostMapping("/upload2") public String upload (MultipartFile[] files, HttpServletRequest request) {String realPath = request.getServletContext().getRealPath("/" );String format = sdf.format(new Date ());new File (path);if (!folder.exists()){try {for (MultipartFile file : files) {String oldName = file.getOriginalFilename();String newName = UUID.randomUUID().toString()+oldName.substring(oldName.lastIndexOf("." ));new File (folder,newName));"://" +request.getServerName()+":" +request.getServerPort()+format+newName;return s;catch (IOException e) {return "" ;
独立多文件 controller如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 @RestController public class FileUploadController3 {new SimpleDateFormat ("/yyyy/mm/dd/" );@PostMapping("/upload3") public String upload (MultipartFile file1, MultipartFile file2,HttpServletRequest request) {String realPath = request.getServletContext().getRealPath("/" );String format = sdf.format(new Date ());new File (path);if (!folder.exists()){try {String oldName1 = file1.getOriginalFilename();String newName1 = UUID.randomUUID().toString() + oldName1.substring(oldName1.lastIndexOf("." ));new File (folder, newName1));String s = request.getScheme() + "://" + request.getServerName() + ":" + request.getServerPort() + format + newName1;String oldName2 = file2.getOriginalFilename();String newName2 = UUID.randomUUID().toString()+oldName2.substring(oldName1.lastIndexOf("." ));new File (folder,newName2));"://" +request.getServerName()+":" +request.getServerPort()+format+newName2;catch (IOException e) {return "" ;
Spring boot+AJAX文件上传 与之前类似,但需要记得配置jq的script,以及编写函数时不要出现错误。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > Title</title > <script src ="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.7.0.js" integrity ="sha256-JlqSTELeR4TLqP0OG9dxM7yDPqX1ox/HfgiSLBj8+kM=" crossorigin ="anonymous" > </script > </head > <body > <div id ="result" > </div > <input type ="file" id ="file" > <input type ="button" value ="上传" onclick ="uploadFile()" > <script language ="JavaScript" > function uploadFile ( var file = $("#file" )[0 ].files [0 ]; var formData =new FormData (); formData.append ("file" ,file); $.ajax ({ type :'post' , url :'/upload' , processData :false , contentType :false , data :formData, success :function (msg ) { $("#result" ).html (msg); } }) } </script > </body > </html >
ControllerAdvice注解的使用 练习在controlleradvice和static_resources中
@ControllerAdvice有三方面的功能:
全局异常处理
全局数据绑定
全局数据预处理
全局异常处理 分别有以下俩种形式
1 2 3 4 @ControllerAdvice @RestControllerAdvice
这里使用第二种进行练习
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 @RestControllerAdvice public class MyGlobalException {@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class) public ModelAndView customException (Exception e) {ModelAndView mv = new ModelAndView ("javaboy" );"error" ,e.getMessage());return mv;
全局数据绑定 ModelAttribute
后面用到了ModelAttribute注解,主要有两个作用
在数据回显时,给变量定义别名
定义全局数据
当用户访问当前Controller中的任意一个方法,在返回数据时,都会将添加了@ModelAttribute注解的方法的返回值,一起返回给前端
编写自定义的Data类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 @ControllerAdvice public class MyGlobalData {@ModelAttribute public Map<String,String> mydata () {new HashMap <>();"username" ,"javaboy" );"address" ,"www.javaboy.org" );return info;
如此一来info便成为了全局变量,在hellocontroller中便可以进行调用了。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 @RestController public class HelloController {@GetMapping("/hello") public void hello (Model model) {"map" );for (String s:keySet){"+---+" +info.get(s));
请求全局数据预处理 在发送请求时,可能遇到接口设计不当导致,出现命名冲突,此时可以通过全局数据预处理进行修复。
controllerAdvice
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 @ControllerAdvice public class MyGlobalData {@InitBinder("a") public void a (WebDataBinder binder) {"a." );@InitBinder("b") public void b (WebDataBinder binder) {"b." );
对应的controller类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 @RestController public class BookController {@PostMapping("/book") public void addBook (@ModelAttribute("b") Book book,@ModelAttribute("a") Author author) {"book=" +book);"author=" +author);
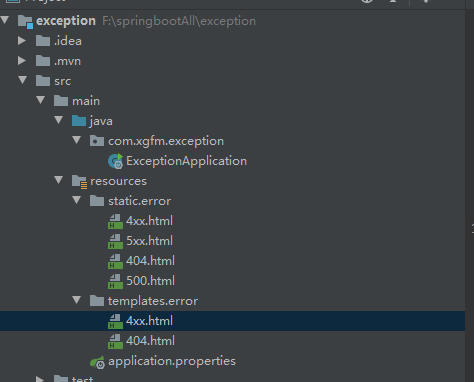
异常页面定义 404问题自动寻找异常页面的优先级,其他同理
(精确高于模糊,动态高于静态)
templates/error/404.html
static/error/404.html
templates/error/4xx.html
static/error/4xx.html
动态定义异常页面 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" xmlns:th ="http://www.thymeleaf.org" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > Title</title > </head > <body > <h1 > 500-templates</h1 > <table > <tr > <td > path</td > <td th:text ="${path}" > </td > </tr > <tr > <td > error</td > <td th:text ="${error}" > </td > </tr > <tr > <td > message</td > <td th:text ="${message}" > </td > </tr > <tr > <td > timestamp</td > <td th:text ="${timestamp}" > </td > </tr > <tr > <td > status</td > <td th:text ="${status}" > </td > </tr > </table > </body > </html >
这样可以将异常以表格的方式输出到前端页面。
自定义异常 通常是不需要的,因为springboot提供的异常已经足够使用了。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 @Component public class MyErrorAttributes extends DefaultErrorAttributes {@Override public Map<String, Object> getErrorAttributes (WebRequest webRequest, ErrorAttributeOptions options) {super .getErrorAttributes(webRequest, options);if ((Integer) map.get("status" )==404 ){"message" ,"页面不存在" );return map;
首先继承DefaultErrorAttributes然后根据现呈的数据进行定义修改或者添加,一般是没有必要去重写BasicErrorController。
同时也可以去自定义视图。
跨域问题 明确了解域的概念
域:协议+域名/IP+端口
如果三个中有不一样的,则说明跨域了。
方法一:添加注解 1 @CrossOrigin(value = "http://localhost:8081",maxAge = 1800)
其后可以添加限制条件等其他
添加在类上说明类中的所有方法都可以,在方法上则对单独的方法有效
方法二:编写WebMvcConfig 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 @Configuration public class WebMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {@Override public void addCorsMappings (CorsRegistry registry) {"/**" )"*" )"*" )"http://localhost:8081" )1800 );
编写config组件,修改响应头
方法三:注入corsfilter 使用Bean注释,将corsFilter注入到spring容器之中
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 @Configuration public class WebMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {@Bean corsFilter () {new UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource ();new CorsConfiguration ();"http://localhost:8081" );"*" );"/**" ,cfg);return new CorsFilter (source);
Spring boot导入XML配置 1 @ImportResource("classpath:beans.xml")
在Application中输入如上的注释即可完成,注入。
拦截器 与过滤器比较像,我们可以使用拦截器做很多工作
拦截器类编写
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 package com.xgfm.interceptor;import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerInterceptor;import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;public class MyInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {@Override public boolean preHandle (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {"preHandle" );return true ;@Override public void postHandle (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {"postHandle" );@Override public void afterCompletion (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {"afterCompletion" );
preHandle
postHandle
afterCompletion
然后配置WebMvcConfig
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 package com.xgfm.interceptor;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.InterceptorRegistry;import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;@Configuration public class WebMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {@Override public void addInterceptors (InterceptorRegistry registry) {new MyInterceptor ()).addPathPatterns("/**" ).excludePathPatterns("/hello" );
addPathPatterns为添加拦截路径。
excludePathPatterns为添加白名单。
最后使用HelloController进行测试
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 package com.xgfm.interceptor;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;@RestController public class HelloController {@GetMapping("/hello") public String hello () {return "hello interceptor" ;@GetMapping("/hello2") public String hello2 () {return "hello2 interceptor" ;
当访问hello时,并没控制台输出
当访问hello2时,控制输出如下
preHandle
即调用了拦截器
系统启动任务 CommandLineRunner 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 @Component @Order(100) public class MyCommandLineRunner01 implements CommandLineRunner {@Override public void run (String... args) throws Exception {"args1 = " + Arrays.toString(args));
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 @Component @Order(99) public class MyCommandLineRunner02 implements CommandLineRunner {@Override public void run (String... args) throws Exception {"args2 = " + Arrays.toString(args));
开机自启动任务
ApplicationRunner 与commandLineRunner一起进行练习,因为比较相似。
二者功能和用法是类似的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 @Component @Order(98) public class MyApplicationRunner implements ApplicationRunner {@Override public void run (ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception {"nonOptionArgs1 = " + nonOptionArgs);for (String optionName : optionNames) {"-1->" + args.getOptionValues(optionName));"sourceArgs1 = " + Arrays.toString(sourceArgs));
Springboot+Web组件 Servlet类 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 @WebServlet(urlPatterns = "/hello") public class MyServlet extends HttpServlet {@Override protected void doGet (HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {super .doGet(req, resp);@Override protected void doPost (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {"MyServlet" );
Filter类 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 @WebFilter(urlPatterns = "/*") public class MyFilter implements Filter {@Override public void doFilter (ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {"MyFilter" );
Listener类 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 @WebListener public class MyListener extends RequestContextListener {@Override public void requestInitialized (ServletRequestEvent requestEvent) {"requestInitialized" );@Override public void requestDestroyed (ServletRequestEvent requestEvent) {"requestDestroyed" );
Application中扫描 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 @SpringBootApplication @ServletComponentScan("com.xgfm.webcomponent") public class WebcomponentApplication {public static void main (String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(WebcomponentApplication.class, args);
Spring boot注册过滤器 使用WebFilter和Component注解 但是这样无法定义Filter的优先级
使用Component注解 单单使用Component注解,然后使用Order进行配置优先级。但这样无法配置路径,只能拦截所有的路径
使用FilterConfiguration类和Bean注解 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 @Configuration public class FilterConfiguration {@Bean filter04FilterRegistrationBean04 () {new FilterRegistrationBean <>();90 );new MyFilter04 ());"/*" ));return bean;@Bean filter05FilterRegistrationBean05 () {new FilterRegistrationBean <>();89 );new MyFilter05 ());"/*" ));return bean;
filter正常编写
Springboot路径映射 使用WebMvcConfig进行配置
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 @Configuration public class WebMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {@Override public void addViewControllers (ViewControllerRegistry registry) {"/02" ).setViewName("02" );
使用对应的add方法添加路径进行映射,但这样存在缺陷,其中Model配置的模板无法渲染动态化的数据,会导致页面为静态页面。
参数类型转换 练习内容为usermanager
如果正常写并且使用controller如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 @RestController public class UserController {@PostMapping("/user1") public void addUser (User user) {"user= " +user);
会导致400错误,因为输入数据无法成为user类的实体对象传入,这时候就要定义一个转换器。
MyDataConverter
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 @Component public class MyDataConverter implements Converter <String,Date> {new SimpleDateFormat ("yyyy-mm-dd" );@Override public Date convert (String source) {try {return sdf.parse(source);catch (ParseException e) {return null ;
对输入的一个数据进行转换,使得controller能够接受,然后进入adduser方法
出现如下传参方式
1 2 3 4 @PostMapping("/user2") public void addUser2 (@RequestBody User user) {"user= " +user);
@RequestBody该注释就要使用json格式传入。
post请求,参数可以是key/value形式,也可以是json形式.自定义的类型转换器对key/value形式的参数有效。json形式的参数,不需要类型转换器。json字符串是通过HttpMessageConverter转换为User对象
自定义项目首页和角标 优先找静态然后再找动态,配置webmvcconfig如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 @Configuration public class WebMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {@Override public void addViewControllers (ViewControllerRegistry registry) {"/index" ).setViewName("index" );
角标就在五个放置资源的地方放一个favicon.ico即可,不需要其他的配置
AOP 练习在welcomepage之中
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 package com.xgfm.welcomepage;import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Component @Aspect public class LogAspect {@Pointcut("execution(* com.xgfm.welcomepage.UserService.*.*(..))") public void pc1 () {@Before("pc1()") public void before (JoinPoint jp) {String name = jp.getSignature().getName();"方法开始执行了" );@After("pc1()") public void After (JoinPoint jp) {String name = jp.getSignature().getName();"方法执行结束了" );@AfterReturning(value = "pc1()",returning = "s") public void afterReturning (JoinPoint jp,String s) {String name = jp.getSignature().getName();"方法返回值是 " + s);@AfterThrowing(value = "pc1()",throwing = "e") public void afterThrowing (JoinPoint jp,Exception e) {String name = jp.getSignature().getName();"方法抛出了异常 " + e);@Around("pc1()") public Object around (ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) {try {Object proceed = pjp.proceed();catch (Throwable e) {return null ;
jdbcTemplate 1 2 3 4 5 <dependency > <groupId > mysql</groupId > <artifactId > mysql-connector-java</artifactId > <version > 5.1.48</version > </dependency >
再给一下mysql驱动。
首先需要在application.properties中配置一下数据库的基本信息
1 2 3 4 spring.datasource.username =root spring.datasource.password =1234 spring.datasource.url =jdbc:mysql:///test01?serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&useSSL=false
另外上述配置完,我的电脑依旧会报错,然后我另外添加了这个
1 spring.datasource.driver-class-name =com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
结果就能够运行了
编写的service
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 package com.xgfm.jdbctemplate.service;import com.xgfm.jdbctemplate.model.User;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;import org.springframework.jdbc.core.PreparedStatementCreator;import org.springframework.jdbc.core.RowMapper;import org.springframework.jdbc.support.GeneratedKeyHolder;import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;import java.sql.*;import java.util.List;@Service public class UserService {@Autowired public int addUser (User user) {int result=jdbcTemplate.update("insert into user (username,address) values(?,?)" ,user.getUsername(),user.getAddress());return result;public int addUser2 (User user) {new GeneratedKeyHolder ();int update = jdbcTemplate.update(new PreparedStatementCreator () {@Override public PreparedStatement createPreparedStatement (Connection con) throws SQLException {PreparedStatement ps = con.prepareStatement("insert into user (username,address) values(?,?)" , Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS);1 , user.getUsername());2 , user.getAddress());return ps;return update;public int deleteById (Long id) {return jdbcTemplate.update("delete from user where id=?" ,id);public int updateById (Long id,String username) {return jdbcTemplate.update("update user set username=? where id = ?" ,username,id);public List<User> getAllUsers () {"select * from user" , new RowMapper <User>() {@Override public User mapRow (ResultSet resultSet, int rowNum) throws SQLException {String username = resultSet.getString("username" );String address = resultSet.getString("address" );String id = resultSet.getString("id" );User user = new User ();return user;return query;
并且运用test进行测试
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 package com.xgfm.jdbctemplate;import com.xgfm.jdbctemplate.model.User;import com.xgfm.jdbctemplate.service.UserService;import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;import java.util.List;@SpringBootTest class JdbctemplateApplicationTests {@Autowired @Test void contextLoads () {new User ();"xgfm" );"xgfmccc" );int i = userService.addUser(user);@Test void test1 () {new User ();"lxm" );"xiaomengege" );int i = userService.addUser2(user);"i= " +i);"user.getId()= " +user.getId());@Test void test2 () {9L );5L ,"lxm" );@Test void test3 () {for (User allUser : allUsers) {
这部分与jbdc非常类似,所以就不额外再记录什么了
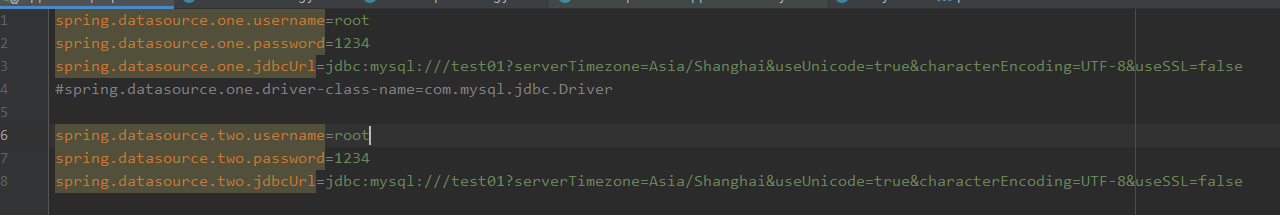
jdbcTemplate多数据源
像这样配置2个,用two和one加在中间进行区分,然后配置DataSourceConfig和JdbcTemplateConfig进行导入配置。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 package com.xgfm.jdbctemplatemulti.config;import com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource;import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import javax.sql.DataSource;@Configuration public class DataSourceConfig {@Bean @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.one") dsOne () {return new HikariDataSource ();@Bean @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.two") dsTwo () {return new HikariDataSource ();
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 package com.xgfm.jdbctemplatemulti.config;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;import javax.sql.DataSource;@Configuration public class JdbcTemplateConfig {@Bean jdbcTemplateOne (@Qualifier("dsOne") DataSource ds) {return new JdbcTemplate (ds);@Bean jdbcTemplateTwo (@Qualifier("dsTwo") DataSource ds) {return new JdbcTemplate (ds);
Spirngboot+MyBatis 先配置properties,然后在Application前添加
1 2 @MapperScan(basePackages = "com.xgfm.mybatis.mapper")
进行包扫描,找出全部的mapper文件
例子:
UserMapper和他的测试类们
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 package com.xgfm.mybatis.mapper;import com.xgfm.mybatis.model.User;import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.*;import java.util.List;public interface UserMapper {@Select("select * from user where id = #{id}") userGetById (Long id) ;@Results({@Result(property = "address",column = "address")}) @Select("select * from user") getAllUsers () ;@Insert("insert into user (username,address) values(#{username},#{address})") @SelectKey(statement = "select last_insert_id()",keyProperty = "id",before = false,resultType = Long.class) addUser (User user) ;@Delete("delete from user where id = #{id}") deleteById (Long id) ;@Update("update user set username = #{username} where id = #{id}") updateById (@Param("username") String username,@Param("id") Long id) ;
这里把@Mapper注释掉是因为在application中配置了包扫描。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 @Autowired @Test void contextLoads () {User user = userMapper.userGetById(5L );@Test void test02 () {new User ();"siyuan" );"cenima" );Long id = user.getId();
测试类
Spirngboot+MyBatis(XML) mapper
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd" > <mapper namespace ="com.xgfm.mybatis.mapper.UserMapper2" > <resultMap id ="UserMap" type ="com.xgfm.mybatis.model.User" > <id property ="id" column ="id" /> <result property ="username" column ="username" /> <result property ="address" column ="address" /> </resultMap > <select id ="userGetById" resultMap ="UserMap" > </select > <select id ="getAllUsers" resultMap ="UserMap" > </select > <insert id ="addUser" parameterType ="com.xgfm.mybatis.model.User" useGeneratedKeys ="true" keyProperty ="id" > </insert > <delete id ="deleteById" > </delete > <update id ="updateById" > </update > </mapper >
mapper接口
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 package com.xgfm.mybatis.mapper;import com.xgfm.mybatis.model.User;import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.*;import java.util.List;public interface UserMapper2 {userGetById (Long id) ;getAllUsers () ;addUser (User user) ;deleteById (Long id) ;updateById (@Param("username") String username, @Param("id") Long id) ;
可以将xml映射文件放置到java的mapper中去,此时就需要在pom.xml文件之中
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 <resources > <resource > <directory > src/main/java</directory > <includes > <include > **/*.xml</include > </includes > </resource > <resource > <directory > src/main/resources</directory > </resource > </resources >
如果想把xml直接放置在resources的mapper下,可以在properties中配置
1 mybatis.mapper-locations =classpath:mappers/*.xml
Mybatis多数据源 首先配置config
与jdbcTemplate相同的DataSourceConfig
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 @Configuration public class DataSourceConfig {@Bean @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.one") dsOne () {return new HikariDataSource ();@Bean @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.two") dsTwo () {return new HikariDataSource ();
完成DataSource的创建
配置MybatisConfigOne和MybatisConfigTwo
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 package com.xgfm.mybatismulti.config;import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean;import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate;import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import javax.sql.DataSource;@Configuration @MapperScan(basePackages = "com.xgfm.mybatismulti.mapper1",sqlSessionFactoryRef ="sqlSessionFactory1",sqlSessionTemplateRef = "sqlSessionTemplate1") public class MybatisConfigOne {@Autowired @Qualifier("dsOne") @Bean sqlSessionFactory1 () {null ;try {SqlSessionFactoryBean bean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean ();catch (Exception e) {return sqlSessionFactory;@Bean sqlSessionTemplate1 () {return new SqlSessionTemplate (sqlSessionFactory1());
需要注意的是添加包扫描注释
创建mapper1和mapper2分别存储不同的mapper文件,与mybatisxml类似,这里就不记录了,但还是需要在resoures同目录配置,否则会找不到(因为我比较喜欢在resources下放xml)
与mybatis一样写映射文件即可
Mybatis主从复制、JPA docker搭建2个mysql,然后修改mysqld.cnf改不明白,先跳过了
Redis 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 @SpringBootTest class RedisApplicationTests {@Autowired @Autowired @Test void contextLoads () {User user = new User ();"xgfm" );"xgfmccc" );ValueOperations ops = redisTemplate.opsForValue();"u" ,user);User u = (User) ops.get("u" );@Test void test1 () {"xgfm" ,"xgfmccc" );String xgfm = ops.get("xgfm" );"xgfm = " + xgfm);
给一些kongzhitai代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 it redis redis-clikeys *123
Session共享 将tomcat的session存入redis之中,三个tomcat就可以共用一个session
引入session,web,redis依赖
在8080和8081端口都开启服务,发现8081可以获取到8080的session中的数据,这是因为spring session使用代理过滤器,将所有的session操作拦截,自动同步至redis之中,也同时自动的从redis之中读取数据。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;@RestController public class HelloController {@Value("${server.port}") @GetMapping("/set") public String set (HttpSession session) {"xgfm" ,"xgfmccc" );return String.valueOf(port);@GetMapping("/get") public String get (HttpSession session) {"xgfm" );return xgfm+":" +port;
最主要的是要引入spring session的依赖才能实现该功能。
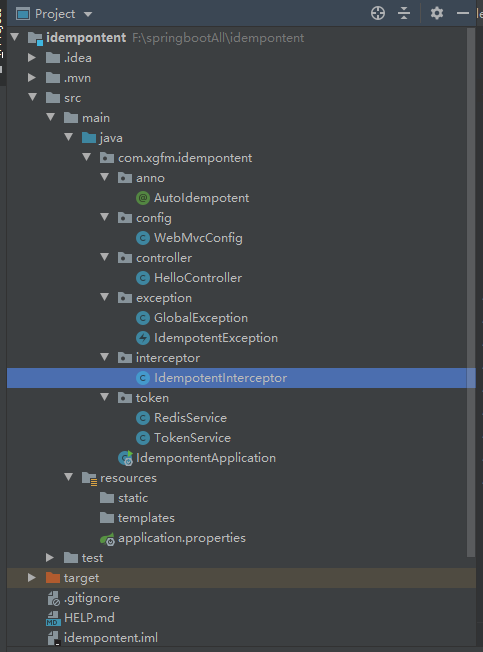
redis处理接口幂等性
要编写的东西有这些
机制就是自定义注释
1 2 3 4 @Target(ElementType.METHOD) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface AutoIdempotent {
然后创建拦截器,在拦截器之中检查有没有带上token,如果没有则通过自定义异常来抛出token相关问题。如果有token或者该方法没有使用自定义的注释(即该方法不需要幂等性,不需要检查有无token)则返回true,进行下一步。
再放一下拦截器
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 @Component public class IdempotentInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {@Autowired @Override public boolean preHandle (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {if (!(handler instanceof HandlerMethod)){return true ;Method method = ((HandlerMethod) handler).getMethod();AutoIdempotent annotation = method.getAnnotation(AutoIdempotent.class);if (annotation!=null ){try {return tokenService.checkToken(request);catch (IdempotentException e) {throw e;return true ;
其中的token则是用UUID生成,用tokenService和RedisService进行检查。
再放一下俩个service
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 package com.xgfm.idempontent.token;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;import org.springframework.data.redis.core.ValueOperations;import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;@Service public class RedisService {@Autowired public boolean setEx (String key,String value,Long expireTime) {boolean result=false ;try {true ;catch (Exception e) {return result;public boolean exists (String key) {return stringRedisTemplate.hasKey(key);public boolean remove (String key) {if (exists(key)){return stringRedisTemplate.delete(key);return false ;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 package com.xgfm.idempontent.token;import com.xgfm.idempontent.exception.IdempotentException;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders;import org.springframework.http.HttpRequest;import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;import java.util.UUID;@Service public class TokenService {@Autowired public String createToken () {10000L );return uuid;public boolean checkToken (HttpServletRequest request) throws IdempotentException {String token = request.getHeader("token" );if (StringUtils.isEmpty(token)){"token" );if (StringUtils.isEmpty(token)){throw new IdempotentException ("token 不存在" );if (!redisService.exists(token)){throw new IdempotentException ("重复操作!" );boolean remove = redisService.remove(token);if (!remove){throw new IdempotentException ("重复操作!" );return true ;
RESTful简介 REST是一种Web软件架构风格,是一种风格,并不是标准。匹配或兼容这种架构风格的网络服务称为REST服务。在SpringBoot中构建RESTful非常容易,因为其提供了自动化配置方案。
快速构建RESTful应用 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 @Entity(name="user") public class User {@Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY) private Long id;private String username;private String address;
创建model并且添加如上注释
再添加一个空的dao层
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 package com.xgfm.restful.dao;import com.xgfm.restful.model.User;import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;public interface UserDao extends JpaRepository <User,Long> {
然后就可以直接通过访问路径进行相对的操作了,非常方便
查询 get
1 http:// localhost:8080 /users/ 1
添加 post/json添加数据
1 http:// localhost:8080 /users
修改 put/json
1 http:// localhost:8080 /users/ 8
分页查询 1 http://localhost:8080/users?page=0&size=3&sort =id ,desc
RESTful定制操作 @RestResource注解 自定义一些数据库操作在userDao中定义声明方法,不用写对应的实现,但要满足对应的要求
1 2 3 4 public interface UserDao extends JpaRepository <User,Long> {findUserByUsernameIs (@Param("username") String username) ;
可以添加@RestResource来选择暴露的路径
1 2 @RestResource(path = "byname") findUserByUsernameIs (@Param("username") String username) ;
比如这样之后,访问查询路径就不再是…/findUserByUsernameIs{?username}而是…/byname{?username}了
这个注解还能够屏蔽原有的方法
比如我想要屏蔽deleteById,只需要重写该方法并且注释给定exported值为false
1 2 3 @Override @RestResource(exported = false) void deleteById (Long along) ;
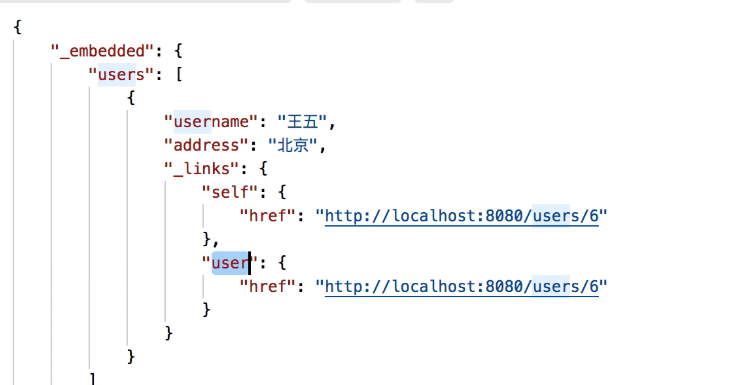
@RepositoryRestResource注解 path,默认类名为users,例如修改为people,那么路径中的users要改为users
collectionResourceRel指的是下图users处
itemResourceRel指的是下图蓝色处
Spring Cache 传统SSM中就可以使用
是缓存体系的抽象实现
@EnableCaching
@Cacheable
@CachePut
@CacheEvict
@Caching
@CacheConfig
配置redis的properties
@EnableCaching 在application中添加该注解,开启缓存功能
参数使用的基本都是默认即可
@Cacheable 1 @Cacheable(cacheNames = "star")
对应方法开启缓存,需要添加cacheNames(前缀)否则会报错,默认情况下该参数也会作为缓存的key
@CacheConfig 这个注解在类上使用,用来描述该类中所有方法使用的缓存key,也可以不使用该注解,直接在方法前使用@Cacheable
Spring Cache自定义缓存key 如果方法存在多个参数,则默认情况下多个参数共同作为缓存的key。
也可以自己指定:在@Cacheable中的key的参数设置为#参数名
也可以使用SPEL表达式
同时也可以完全进行自定义key
创建MyKeyGenerator自定义类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 @Component public class MyKeyGenerator implements KeyGenerator {@Override public Object generate (Object target, Method method, Object... params) {":" +method.getName()+":" + Arrays.toString(params);return s;
在service中进行使用
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 @Service public class UserService {@Autowired @Cacheable(cacheNames = "star" ,keyGenerator = "myKeyGenerator") public User getUserById (Long id) {"getById" +id);User user = new User ();"xgfm" );return user;
更新缓存 在service中添加方法,如果缓存不存在则进行缓存,存在则进行更新
1 2 3 4 @CachePut(cacheNames = "c1",key="#user.id") public User updateUserById (User user) {return user;
清空缓存 在service中添加方法
1 2 3 4 @CacheEvict(cacheNames = "c1") public void deleteUserById (Long id) {"deleteByUserId" );
Spring Security 安全管理!
1 2 3 4 <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId > </dependency >
添加该依赖后,项目中的所有接口都被保护起来了
输入接口后会自动跳转至login
账号:admin 密码:在控制台会出现一次性密码
Using generated security password: ab460a73-3b0b-4198-bf8c-1ef300062254
HttpSecurity配置 目前的直接配置是对所有的接口进行拦截,实际上肯定是行不通的,是需要配置类似白名单的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 @Override public void configure (HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {"/admin/**" ).hasRole("admin" )"user/**" ).hasAnyRole("admin" ,"user" )"/doLogin" )
如此配置完成之后,admin可以访问admin和user的网页,而user只能访问user的网页。
先放一下,这套springSecurtiy好像有点老旧
WebSocket 使用HTTP端口进行连接可以避免被拦截
websocket支持跨域连接
Spring boot +WebSocket 聊天室 选择web和websocket依赖。
如果是单聊需要存在用户的概念,需要登录
而点对面就不需要登录了。
这里使用webJar,依赖如下:
1 2 3 4 5 <dependency > <groupId > org.webjars</groupId > <artifactId > stomp-websocket</artifactId > <version > 2.3.3</version > </dependency >
再加上jquery的依赖
1 2 3 4 5 <dependency > <groupId > org.webjars</groupId > <artifactId > jquery</artifactId > <version > 3.5.1</version > </dependency >
以及添加locator core的依赖
1 2 3 4 5 <dependency > <groupId > org.webjars</groupId > <artifactId > webjars-locator-core</artifactId > <version > 0.46</version > </dependency >
还有这个依赖
1 2 3 4 5 <dependency > <groupId > org.webjars</groupId > <artifactId > sockjs-client</artifactId > <version > 1.1.2</version > </dependency >
编写WebSocketConfig继承WebSocketMessageBrokerConfigurer接口重写registerStompEndpoints和configureMessageBroker方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 package com.xgfm.chat01.config;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import org.springframework.messaging.simp.config.MessageBrokerRegistry;import org.springframework.web.socket.config.annotation.EnableWebSocketMessageBroker;import org.springframework.web.socket.config.annotation.StompEndpointRegistry;import org.springframework.web.socket.config.annotation.WebSocketMessageBrokerConfigurer;@Configuration @EnableWebSocketMessageBroker public class WebSocketConfig implements WebSocketMessageBrokerConfigurer {@Override public void registerStompEndpoints (StompEndpointRegistry registry) {"/chat" ).withSockJS();@Override public void configureMessageBroker (MessageBrokerRegistry registry) {"/topic" );
编写controller
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 package com.xgfm.chat01.controller;import com.xgfm.chat01.model.Message;import org.springframework.messaging.handler.annotation.MessageMapping;import org.springframework.messaging.handler.annotation.SendTo;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;@Controller public class GreetingController {@MessageMapping("/hello") @SendTo("/topic/greetings") public Message greeting (Message message) {return message;
然后编写message的model,属性为username和content,分别为发送人和发送信息内容
在resources中的static中编写模型
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > Title</title > <script src ="/webjars/jquery/jquery.min.js" > </script > <script src ="/webjars/sockjs-client/sockjs.min.js" > </script > <script src ="/webjars/stomp-websocket/stomp.min.js" > </script > </head > <body > <div > <label for ="username" > 请输入用户名:</label > <input type ="text" id ="username" placeholder ="用户名" > </div > <div > <input type ="button" value ="连接" id ="connect" > <input type ="button" value ="断开连接" id ="disconnect" disabled ="disabled" > </div > <div id ="chat" > </div > <div > <label for ="content" > 请输入聊天内容</label > <input type ="text" id ="content" placeholder ="聊天内容" > </div > <input type ="button" id ="send" value ="发送" disabled ="disabled" > <script > var stompClient; $(function ( $("#connect" ).click (function ( connect (); $("#send" ).click (function ( stompClient.send ("/hello" ,{},JSON .stringify ({"name" :$("#username" ).val (),"content" :$("#content" ).val ()})) }) $("#disconnect" ).click (function ( stompClient.disconnect (); setConnect (false ); }) }) }) function connect ( if (!$("#username" ).val ()){ return ; } var socketjs=new SockJS ("/chat" ); stompClient=Stomp .over (socketjs); stompClient.connect ({},function (frame ) { setConnect (true ); stompClient.subscribe ("/topic/greetings" ,function (greeting ) { var msgContent=JSON .parse (greeting.body ); $("#chat" ).append ("<div>" +msgContent.name +":" +msgContent.content +"</div>" ); }); }) } function setConnect (connected ) { $("#connect" ).prop ("disabled" ,connected); $("#disconnect" ).prop ("disabled" ,!connected); $("#send" ).prop ("disabled" ,!connected); } </script > </body > </html >
完成。
消息中间件 先咕咕咕一下,等会补上
邮件发送基础知识 SMTP 协议全称为 Simple Mail Transfer Protocol,译作简单邮件传输协议,它定义了邮件客户端软件与 SMTP 服务器之间,以及 SMTP 服务器与 SMTP 服务器之间的通信规则。
而 POP3 协议全称为 Post Office Protocol ,译作邮局协议,它定义了邮件客户端与 POP3 服务器之间的通信规则
发送QQ邮件准备工作 首先需要打开邮箱–账户–SMTP服务开启,从而获取授权码
发送邮件 发送简单邮件 在application.properties中配置相关信息
properties配置:(需要注意的是username是qq邮箱地址,而password不是密码,是授权码)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 spring.mail.host =smtp.qq.com spring.mail.port =465 spring.mail.username =获取到授权码的QQ邮箱 spring.mail.password =授权码 spring.mail.default-encoding =utf-8 spring.mail.properties.mail.smtp.socketFactory.class =javax.net.ssl.SSLSocketFactory spring.mail.properties.mail.debug =true
测试–方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 @Autowired @Test void contextLoads () {new SimpleMailMessage ();"发件人邮箱(properties中的邮箱)" );"收件人的邮箱" );new Date ());"邮件主题-测试邮件" );"邮件内容-测试邮件" );
发送带附件的邮件 需要配置复合邮件类(javaMailSender)使用IO流的file进行文件输入,从而完成附件的携带,其他代码是不变的,只需要修改一下test类即可
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 @Test void test1 () throws MessagingException {File file = new File ("E:\\zp\\xg.jpg" );MimeMessage mimeMessage = javaMailSender.createMimeMessage();MimeMessageHelper helper = new MimeMessageHelper (mimeMessage, true );"发件人邮箱" );"收件人邮箱" );new Date ());"邮件主题-测试邮件" );"邮件内容-测试邮件" );
发送带图片资源的邮件 图片存在于邮件正文之中,而不是附件之中。
需要在setText配置参数true,从而支持html,然后使用html标签中的img标签src进行占位,通过addInLine和File来给占位的地方放置图片,但这种方式并不常用,如果有使用邮件的需求,使用thymeleaf和Freemarker模板会好用很多很多。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 @Test void test2 () throws MessagingException {File file = new File ("E:\\zp\\xg.jpg" );MimeMessage mimeMessage = javaMailSender.createMimeMessage();MimeMessageHelper helper = new MimeMessageHelper (mimeMessage, true );"发件人邮箱" );"收件人邮箱" );new Date ());"邮件主题-测试邮件" );"<div>哥们带图片资源,哥们叼得一</div><div><img src='cid:p01' /></div>" ,true );"p01" ,file);
Freemarker邮件模板 前提准备 编写模板(mail.ftl)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 <div > 欢迎${username}入职${company},您的入职信息如下:</div > <table border ="1" > <tr > <td > 姓名</td > <td > ${username}</td > </tr > <tr > <td > 职位</td > <td > ${position}</td > </tr > <tr > <td > 薪水</td > <td > ${salary}</td > </tr > </table > <div style ="color: red ;font-size: x-large" > 希望在未来的日子里携手奋进!</div >
编写model(User类)
test方法 如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 @Test void test3 () throws MessagingException, IOException, TemplateException {MimeMessage mimeMessage = javaMailSender.createMimeMessage();MimeMessageHelper helper = new MimeMessageHelper (mimeMessage, true );"收件人" );"发件人" );new Date ());"邮件主题-测试邮件" );Configuration cfg = new Configuration (Configuration.VERSION_2_3_30);"mail" );Template template = cfg.getTemplate("mail.ftl" );new User ();"星光浮梦" );"地下魔盗团" );"保安队长" );9999999.0 );StringWriter out = new StringWriter ();String text = out.toString();true );"内容text为 =" +text);
写的过程中出现了一些小失误,把setClassLoaderForTemplateLoading写成了setClassForTemplateLoading,导致一致报错,但是把Class文件导入到setClassForTemplateLoading,也还是会报错,等会研究一下这俩方法。
修改完成后成功发送邮件了。
与thymeleaf不同的在于freemarker模板需要自己配置路径,所以.ftl文件放在哪都差距不大,而Thymeleaf需要放置在templates之中才行,否则需要在properties中配置。
Thymeleaf邮件模板 与freemarker最大区别在于需要注入TemplateEngine这个类。
他可以帮助我们省去很多繁琐的配置过程,美中不足的是他不能直接放入user类,需要自己一个个输入。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 @Autowired @Test void test4 () throws MessagingException, IOException, TemplateException {MimeMessage mimeMessage = javaMailSender.createMimeMessage();MimeMessageHelper helper = new MimeMessageHelper (mimeMessage, true );"1499923379@qq.com" );"1499923379@qq.com" );new Date ());"邮件主题-测试邮件" );new User ();"星光浮梦" );"地下魔盗团" );"保安队长" );9999999.0 );new Context ();"username" ,user.getUsername());"position" ,user.getPosition());"company" ,user.getCompany());"salary" ,user.getSalary());String text = templateEngine.process("mail.html" , ctx);true );
注解配置定时任务 @Schduled 在Application中添加EnableScheduling注解来开启定时任务。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 @Component public class MySchedule {@Scheduled(fixedDelay = 1000) public void fixedDelay () {"fixedDelay:" +new Date ());
scheduled设置为当前任务结束后一秒执行一次,然后该程序就会在控制台不断输出当前任务执行的sout
1 2 3 4 @Scheduled(fixedRate = 1000) public void fixedRate () {"fixedRate:" +new Date ());
fixedRate和fixedDelay的区别在于fixedRate是在任务开启xx时间后执行,而fixedDelay则是在任务执行完xx时间后执行。
1 2 3 4 @Scheduled(initialDelay = 1000,fixedRate = 1000) public void initDelay () {"initDelay:" +new Date ());
而initialDelay则是延迟xx时间后执行。
但延迟定时任务并不能很好的满足全部需求
这时就需要使用cron,cron表达式格式如下;
秒 分 小时 日 月 周 年
1 2 3 4 @Scheduled(cron = "0/5 55 * * * *") public void cron () {"cron:" +new Date ());
该cron的意思为在任何年月日小时的55分钟,每5秒输出一次。
@Quartz注解 一般在项目中,除非定时任务涉及到的业务实在过于简单才会使用@Scheduled注解来解决定时任务,否则大部分情况可能都是使用Quartz来做定时任务的。
创建项目时还需要添加I/O下的Quartz Scheduler依赖。
1 2 3 4 5 6 @Component public class MyJob01 {public void sayHello () {"MyJob01 : " +new Date ());
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public class MyJob02 extends QuartzJobBean {private String name;public String getName () {return name;public void setName (String name) {this .name = name;@Override protected void executeInternal (JobExecutionContext context) throws JobExecutionException {"MyJob02 : " +name+" : " +new Date ());
myjob01是作为组件注入容器,而Myjob02则是继承QuartzJobBean从而直接使用。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 @Configuration public class QuartzConfig {@Bean jobDetail01 () {MethodInvokingJobDetailFactoryBean bean = new MethodInvokingJobDetailFactoryBean ();"myJob01" );"sayHello" );return bean;@Bean jobDetail02 () {JobDetailFactoryBean bean = new JobDetailFactoryBean ();JobDataMap map = new JobDataMap ();"name" ,"xgfm" );return bean;@Bean simpleTriggerFactoryBean () {SimpleTriggerFactoryBean bean = new SimpleTriggerFactoryBean ();3 );1000 );1000 );return bean;@Bean cronTriggerFactoryBean () {CronTriggerFactoryBean bean = new CronTriggerFactoryBean ();"0/5 * * * * ?" );return bean;@Bean schedulerFactoryBean () {SchedulerFactoryBean bean = new SchedulerFactoryBean ();return bean;
前俩个方法为JobDetailFactoryBean但是第一个查找bean时要注意是注入到容器中的bean,首字母需要小写(我就是因为没小写一直not found,不停报错)
然后俩个是定义触发器bean。
最后一个是将两个定义好的触发器加入到schedulerFactoryBean之中。
这些bean都需要添加@Bean注释。
Swagger简介 swagger的作用在于便于进行前后端分离。
它通过一个网站展示接口及其参数,便于前后端进行编写。
它本身就是一个开源项目。
注:Swagger3.0不兼容SpringBoot2.6.x及以上的版本,需要降低springboot的版本。
Swagger2和Swagger3的区别 支持OpenAPI
接口和每个接口的操作
输入参数和响应内容
认证 方法
一些必要的联系信息,license等
依赖 在3.0版本中,只需要一个starter的maven坐标即可完成。
1 2 3 4 5 <dependency > <groupId > io.springfox</groupId > <artifactId > springfox-boot-starter</artifactId > <version > 3.0.0</version > </dependency >
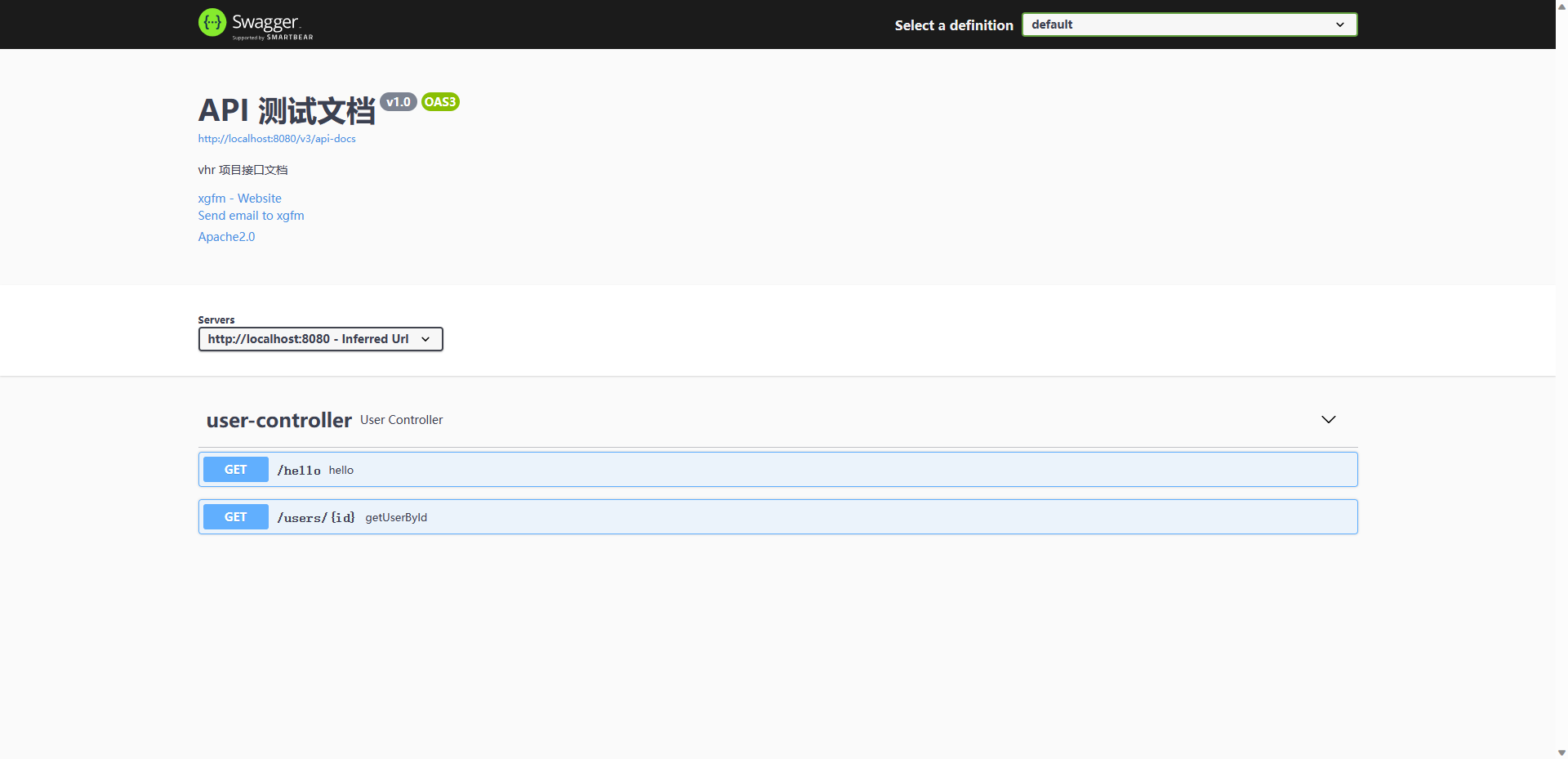
接口地址 文档接口地址和文档页面地址均发生变化。
文档接口地址:http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui/index.html
该网页如下:
注解 3.0提供了一些其他注解。不过2的注解在3中都是可以正常使用的。
Swagger3–HelloWorld 创建userController直接配置hello接口
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 @RestController public class UserController {@GetMapping("/hello") public String hello () {return "hello" ;
然后启动服务,进入文档接口地址就直接会弹出所有的接口及其参数类型。
同时也可以编写SwaggerConfig进行对swagger文档页面进行自定义。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 @Configuration public class SwaggerConfig {@Bean docket () {return new Docket (DocumentationType.OAS_30)"com.xgfm.swagger3.controller" ))new ApiInfoBuilder ()"vhr 项目接口文档" )new Contact ("xgfm" ,"http://xgfm737.github.io" ,"1111@qq.com" ))"v1.0" )"API 测试文档" )"Apache2.0" )"http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0" )
Swagger注解 @ApiOperation和 @Operation 1 2 3 4 5 6 @Operation(summary = "查询用户",description ="根据 id 查询用户" ) @GetMapping("/users/{id}") public String getUserById (@PathVariable Integer id) {return "user: " +id;
二者在使用方法上类似,ApiOperation是swagger2的,而Operation则是3的,用法是基本一致的,第一个参数是方法的作用,第二个参数是注释。
@ApiImplicitParam 1 @ApiImplicitParam(paramType = "path",name = "id",value = "用户id",required = true)
paramType参数可以填写:
path:即放在地址栏之中
query:以key value方法传递
body:参数存在于请求体
但是该行注释只是限制swagger文档接口的用法,并不会对实际上的操作产生其他影响。所以用处较小。
@ApiImplicitParams 1 2 3 4 @ApiImplicitParams({ @ApiImplicitParam(paramType = "path",name = "id",value = "用户id",required = true), @ApiImplicitParam(paramType = "path",name = "uid",value = "用户uid",required = false) })
作用是存放多个参数
@ApiResponses和@ApiResponse 1 2 3 4 @ApiResponses({ @ApiResponse(responseCode = "200",description = "请求成功"), @ApiResponse(responseCode = "500",description = "请求失败") })
格式如上,作用就是定义状态码定义的显示。
@ApiIgnore 如名字所示,直接忽略当前接口。
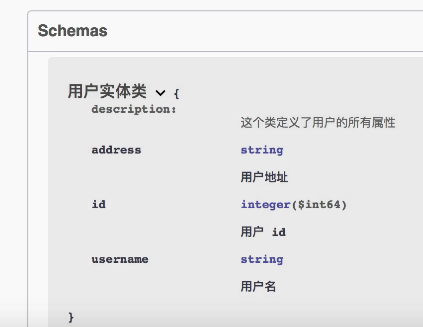
@ApiModelProperty和@ApiModel 这次把model也放出来,是因为需要添加ApiModel(类的解释)和ApiModelProperty(类中属性的解释)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 @ApiModel(value = "用户实体类",description = "这个类定义了用户的所有属性") public class User {@ApiModelProperty("用户id") private Long id;@ApiModelProperty("用户名") private String username;@ApiModelProperty("用户地址") private String address;public Long getId () {return id;public void setId (Long id) {this .id = id;public String getUsername () {return username;public void setUsername (String username) {this .username = username;public String getAddress () {return address;public void setAddress (String address) {this .address = address;@Override public String toString () {return "User{" +"id=" + id +", username='" + username + '\'' +", address='" + address + '\'' +'}' ;
下面的这段是usercontroller中的方法,最主要是@RequestBody的使用。
1 2 3 4 @PostMapping("/user") public String addUser (@RequestBody User user) {return user.toString();
然后该实体类就会有如下的注释:
总结 仍然有一些小bug,但是松哥说是因为swagger3的原因,说不定使用swagger2会有更好的效果?
然后就是这个程序目前对于学生来说可能还是说用处不是很大。
最后附上全部的controller代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 package com.xgfm.swagger3.controller;import com.xgfm.swagger3.model.User;import io.swagger.annotations.ApiImplicitParam;import io.swagger.annotations.ApiImplicitParams;import io.swagger.annotations.ApiOperation;import io.swagger.v3.oas.annotations.Operation;import io.swagger.v3.oas.annotations.Parameter;import io.swagger.v3.oas.annotations.parameters.RequestBody;import io.swagger.v3.oas.annotations.responses.ApiResponse;import io.swagger.v3.oas.annotations.responses.ApiResponses;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;import springfox.documentation.annotations.ApiIgnore;@RestController public class UserController {@GetMapping("/hello") @ApiIgnore public String hello () {return "hello" ;@ApiResponses({ @ApiResponse(responseCode = "200",description = "请求成功"), @ApiResponse(responseCode = "500",description = "请求失败") }) @Operation(summary = "查询用户",description ="根据 id 查询用户" ) @ApiImplicitParam(paramType = "path",name = "id",value = "用户id",required = true) @GetMapping("/users/{id}") public String getUserById (@PathVariable Integer id) {return "user: " +id;@PostMapping("/user") public String addUser (@RequestBody User user) {return user.toString();
数据校验
@Null 被注解的元素必须为 null
@NotNull 被注解的元素必须不为 null
@AssertTrue 被注解的元素必须为 true
@AssertFalse 被注解的元素必须为 false
@Min(value) 被注解的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须大于等于指定的最小值
@Max(value) 被注解的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须小于等于指定的最大值
@DecimalMin(value) 被注解的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须大于等于指定的最小值
@DecimalMax(value) 被注解的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须小于等于指定的最大值
@Size(max=, min=) 被注解的元素的大小必须在指定的范围内
@Digits (integer, fraction) 被注解的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须在可接受的范围内
@Past 被注解的元素必须是一个过去的日期
@Future 被注解的元素必须是一个将来的日期
@Pattern(regex=,flag=) 被注解的元素必须符合指定的正则表达式
@NotBlank(message =) 验证字符串非 null,且长度必须大于0
@Email 被注解的元素必须是电子邮箱地址
@Length(min=,max=) 被注解的字符串的大小必须在指定的范围内
@NotEmpty 被注解的字符串的必须非空
@Range(min=,max=,message=) 被注解的元素必须在合适的范围内
普通校验 前端js校验和服务端校验
Springboot提供了自动化设置。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 private Long id;@Size(min=5,max=8) private String name;@NotNull private String address;@DecimalMin(value="1") @DecimalMax(value = "200") private Integer age;@NotNull @Email private String email;
user实体类添加注解。
并且在controller 类的方法同时也需要添加注释才可以开启校验。
1 2 3 @PostMapping("/user") public void addUser (@Validated User user) {
自定义检验错误 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 private Long id;@Size(min=5,max=8,message = "{user.name.size}") private String name;@NotNull(message = "{user.address.notnull}") private String address;@DecimalMin(value="1",message = "{user.age.min}") @DecimalMax(value = "200",message = "{user.age.max}") private Integer age;@NotNull(message = "{user.email.notnull}") @Email(message = "{user.email.pattern}") private String email;
1 2 3 4 5 6 user.name.size =name长度错了! user.address.notnull =address 不能为空哦 user.age.min =age 最小为1 user.age.max =age 最大为200 user.email.notnull =email 不能为空哦 user.email.pattern =email 格式错误
首先需要创建ValidationMessage.properties。并在其中配置对应的数据检验错误,然后在model中添加message,也可以直接在model的message中写。
分组校验 普通校验是所有的属性进行重复校验效率较低。
而在业务逻辑中有些时候有些校验是不需要进行的。
首先创建两个接口。
然后使得注解分入不同的groups
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 private Long id;@Size(min=5,max=8,message = "{user.name.size}",groups = ValidationGroup1.class) private String name;@NotNull(message = "{user.address.notnull}",groups = ValidationGroup2.class) private String address;@DecimalMin(value="1",message = "{user.age.min}",groups = {ValidationGroup1.class,ValidationGroup2.class}) @DecimalMax(value = "200",message = "{user.age.max}",groups = {ValidationGroup1.class,ValidationGroup2.class}) private Integer age;@NotNull(message = "{user.email.notnull}") @Email(message = "{user.email.pattern}") private String email;
然后在校验接口定义需要校验的组即可。
例如:
1 2 3 @PostMapping("/user") public void addUser (@Validated(ValidationGroup1.class) User user, BindingResult result) {
如此一来就只会去校验属于group1的注释了,在本次例子中的校验group1就只有name和age。
应用监控 先跳一下,因为目前是完全用不着的好像
编译打包 Springboot可以使用默认插件配置spring-boot-maven-plugin
该插件拥有5个功能:
build-info:生成项目的构建信息文件build-info.properties
repackage:在mvn package执行之后,这个命令再次打包生成可执行的jar,同时mvn package生成的jar重名为*origin
run:这个可以用来运行Spring boot应用。
start:这个在 mvn integration-test 阶段,进行 Spring Boot 应用生命周期的管理
stop:这个在 mvn integration-test 阶段,进行 Spring Boot 应用生命周期的管理
这里功能,默认情况下使用就是 repackage 功能,其他功能要使用,则需要开发者显式配置。
打包的jar包分为可执行jar和可依赖jar
默认的生成的为可执行jar,可执行jar不可以被依赖,需要删除mvn的spirng-boot-maven-plugin依赖。
当然也可以将可执行jar和可依赖jar同时生成,mvn配置如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 <build>
exec为可依赖jar,配置中的exec为自动生成的后缀。
xgfm 目前就先这样,接下来会继续写机器学习,开始编写vhr,以及学习一下VM虚拟机相关的,还有Spring Security安全管理的东西。后续有更新或其他理解也会继续上传的。